Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain asexual reproduction in plants.
उत्तर १
Asexual reproduction is the process by which a plant gives rise to a new plant without producing seeds or spores. Asexual reproduction in plants occurs by vegetative propagation. The development of a new plant from the vegetative part of a plant-like stem, root, or leaf is known as vegetative propagation. The various methods of vegetative propagation are:
- From underground stem: A potato plant has an underground stem known as the tuber. It has many buds called eyes. A vegetative bud consists of a short stem, around which immature overlapping leaves are present in a folded state. A bud can give rise to a new plant through asexual reproduction.
- Rhizome: The underground stem of ginger is known as the rhizome which is capable of giving rise to a new plant. A corm is an underground stem as found in Gladiolus. It can also be used for vegetative propagation.
- Through leaves: Leaves perform the function of photosynthesis. However, they can take part in asexual reproduction as well. In some plants, leaves can give rise to a new plant asexually. For example, the leaves of the plant Bryophyllum contain buds on its margins. These buds give rise to a new plant through asexual reproduction.
- From aerial stem: In certain plants, a slender stem arises from the base of the plant and touches the soil, it develops roots and buds at the point of contact with the soil and gives rise to new plants. When the new plant is old enough the stem connecting it to the parent plant withers away.
उत्तर २
- Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction in plants, where new plants are produced from the vegetative parts like roots, stems, leaves, and buds.
- All plants produced by vegetative propagation are similar to the parent, as they are produced from a single parent.
- This process can be observed in potato where new plants develop from eyes (bud on potato) or Bryophyllum which reproduces from buds on the leaf margin. Sugarcane and grasses also reproduce by buds present on nodes. Carrot and radish perform vegetative reproduction with the help of roots.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation.
What is multiple fission?
Name the following : 'Blobs' that develop at the tips of the non-reproductive threads in Rhizopus.
Explain how non-reproductive structures protect themselves and what is the function of the structures released from the 'blobs' in Rhizopus.
List any two modes of asexual reproduction in animals.Under which mode of reproduction is vegetative propagation placed and why?
How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Name the method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Name the process by which an Amoeba reproduces. Draw the various stages of its reproduction in a proper sequence.
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
Plasmodium reproduces by the process of ............ fission whereas Paramecium reproduces by the process of ......... fission.
Name two plants which are usually propagated by artificial propagation methods. Name the method of artificial propagation used in each case.
What is meant by the term 'fission' as used in biology?
What is a tuber? Name one stem tuber and one root tuber.
One of the following reproduces by forming spores. This in :
(a) Fern
(b) Planaria
(c) Spirogyra
(d) Potato
Asexual reproduction through budding takes place in :
(i) Amoeba and Yeast
(ii) Yeast and Hydra
(iii) Hydra and Plasmodium
(iv) Corals and Sponges
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) only (ii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Vegetative propagation refers to the formation of new plants from the following existing organs of the old plants :
(a) stems, roots and flowers
(b) stems, roots and leaves
(c) stems, flowers and fruits
(d) stems, leaves and flowers
The two organisms which can regenerate fully from their cut body parts are :
(a) Paramecium and Hydra
(b) Hydra and Amoeba
(c) Planaria and Leishmania
(d) Hydra and Planaria
Differentiate between the following:
Cutting and grafting
Define the following:
Vegetative reproduction
Mention the common method of reproduction in Bougainvillea.
What is vegetative propagation? List with brief explanation three advantages of practising this process for growing some types of plants. Select two plants from the following which are grown by this process:
Banana, Wheat, Mustard, Jasmine, Gram.
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba draws the following diagrams. However these diagrams are not in proper sequence: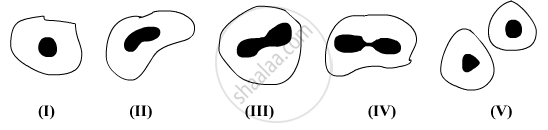
The correct sequence is:
(A) I, V, IV, III, II
(B) I, III, IV, V, II
(C) I, V, III, IV, II
(D) I, IV, V, III, II
Select the correct statements for the process of budding in yeast:
I. A bud arises from a particular region on a parent body.
II. A parent cell divides into two daughter cells, here the parental identity is lost.
III. Before detaching from the parent body a bud may form another bud.
IV. A bud when detaches from the parent body grows into a new individual.
(A) I, II and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and I
(D) IV, I and II
A student after viewing a prepared slide illustrates the budding in yeast in the following order which is not correct:

(A) b, c, d, e, a
(B) b, e, d, c, a
(C) b, d, e, c, a
(D) b, d, c, e, a
A student has to observe a permanent slide of binary fission in Amoeba. Find the correct sequence of steps given below for focussing the object under a microscope.
(a) Place the slide on the stage, look through the eye-piece and adjust the mirror to get proper illumination.
(b) Focus the slide sharp using fine adjustment screw
(c) Look through the eye-piece and raise the objective lens using coarse adjustment screw till the object is focussed.
(d) Look through the eye-piece and move the slide till the object is visible.
(A) d, c, b, a
(B) a, b, d, c
(C) a, d, c, b
(D) a, c, d, b
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
Ramesh observed a slide of Amoeba with elongated nuclei. It would represent _______________.
Define vegetative propagation. List its two methods.
Name the parts of the plants used to grow following flower: Dahlia
Give the name of the plant that reproduces vegetatively by: Leaves
What do you understand by hybridisation?
Describe the process of fertilization in angiosperms with the help of a diagram.
Asexual reproduction occurs by __________ cell division.
Identify the type of reproduction from the following explanation and draw a neat and labelled diagram.
- The body of the parent organism breaks up into many fragments and each fragment starts to live as an independent new organism.
- Give two examples of living organisms which follow this type of reproduction method.
Yeast reproduces asexually by means of multiple fission.
By which of the following egg in female gametophyte is accompanied?
During favourable conditions, Amoeba reproduces by ______
In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by
Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
- Flowers are always bisexual
- They are the sexual reproductive organs
- They are produced in all groups of plants
- After fertilisation they give rise to fruits
When you keep food items like bread and fruits outside for a long time, especially during the rainy season, you will observe a cottony growth on them.
How does the growth take place?
In the diagram of a bisexual flower given in Figure 12.5, draw the missing part and label the parts marked (a), (b) and (c). Also, label the missing part that you draw

