Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain asexual reproduction in plants.
उत्तर १
Asexual reproduction is the process by which a plant gives rise to a new plant without producing seeds or spores. Asexual reproduction in plants occurs by vegetative propagation. The development of a new plant from the vegetative part of a plant-like stem, root, or leaf is known as vegetative propagation. The various methods of vegetative propagation are:
- From underground stem: A potato plant has an underground stem known as the tuber. It has many buds called eyes. A vegetative bud consists of a short stem, around which immature overlapping leaves are present in a folded state. A bud can give rise to a new plant through asexual reproduction.
- Rhizome: The underground stem of ginger is known as the rhizome which is capable of giving rise to a new plant. A corm is an underground stem as found in Gladiolus. It can also be used for vegetative propagation.
- Through leaves: Leaves perform the function of photosynthesis. However, they can take part in asexual reproduction as well. In some plants, leaves can give rise to a new plant asexually. For example, the leaves of the plant Bryophyllum contain buds on its margins. These buds give rise to a new plant through asexual reproduction.
- From aerial stem: In certain plants, a slender stem arises from the base of the plant and touches the soil, it develops roots and buds at the point of contact with the soil and gives rise to new plants. When the new plant is old enough the stem connecting it to the parent plant withers away.
उत्तर २
- Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction in plants, where new plants are produced from the vegetative parts like roots, stems, leaves, and buds.
- All plants produced by vegetative propagation are similar to the parent, as they are produced from a single parent.
- This process can be observed in potato where new plants develop from eyes (bud on potato) or Bryophyllum which reproduces from buds on the leaf margin. Sugarcane and grasses also reproduce by buds present on nodes. Carrot and radish perform vegetative reproduction with the help of roots.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between 'stem tuber' and 'tuberous root'.
How the process of regeneration in Planaria process different from reproduction?
Study the following diagrams showing various stages of binary fission in Amoeba:
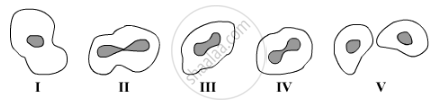
The correct sequence of these diagrams should be:
(A) I, IV, III, II, V
(B) I, III, IV, II, V
(C) I, II, IV, III, V
(D) I, II, III, IV, V
State two disadvantages of vegetative propagation?
Name the asexual method of reproduction in Hydra
Name the natural method by which strawberry plants are propagated.
What is meant by the term 'artificial propagation of plants'?
What is a tuber? Name one stem tuber and one root tuber.
How does an Amoeba reproduce? Describe the process of reproduction in Amoeba with the help of labelled diagrams of different stages in its reproduction process.
Name the method by which bread mould (Rhizopus fungus) reproduces. Is this method sexual or asexual?
What is meant by 'grafting' as a means of propagation in plants?
What is the difference between the cuttings method and grafting method for the artificial propagation of plants?
Asexual reproduction through budding takes place in :
(i) Amoeba and Yeast
(ii) Yeast and Hydra
(iii) Hydra and Plasmodium
(iv) Corals and Sponges
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) only (ii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
The thread like structures that develop on a moist slice of bread in Rhizopus are ______.
An alga which reproduces by the asexual reproduction method called fragmentation is :
(a) Rhizopus
(b) Salmonella
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Spirogyra
A tiny animal having tentacles which reproduces by growing buds on the sides of its body is :
(a) Planaria
(b) Yeast
(c) Amoeba
(d) Hydra
The stem of a fruit tree X fixed in soil is cut in a slanting way. The upper part of stem of another fruit tree Y of different variety of same species is also cut in a slanting way. The cut stem of tree Y, without roots but having some leaves, is placed over the rooted cut stem of tree X in such a way that their cut surfaces fit together properly. While joining the two cut stems, care is taken to make sure that the layer Z of one cut stem is in contact with layer Z of the other cut stem. The joint of cut stem is bound tightly with a piece of cloth and covered properly with polythene. Soon the cut heals and the two stems grow together and become one fruit tree producing leaves, flowers and fruits.
(a) What is the name of this method of producing plants or trees?
(b) What name is given to the cut stem of tree X having roots?
(c) What name is given to the cut stem of tree Y which has no roots but has some leaves?
(d) Name the layer Z.
(e) Why should the layer Z of one cut stem be in contact with the layer Z of the other cut stem?
(f) Name any four fruit trees which are usually bred by this technique.
(g) State any one advantage of producing fruit trees by this technique.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The process of fusion of gametes is called .............
Fill in the blank:
Yeast cells reproduce by ________.
Mention the common method of reproduction in Potato.
Choose the correct statement(s) on budding in yeast from the following :
I. A parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells and here the parent identity is lost.
II. In this the elongated nucleus divides to form two or more daughter nuclei.
III. A bud arises from a particular region on a parent body.
IV. After detaching from the parent body the bud grows into a new independent individual.
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) II and III only
(D) III and IV only
What happens when on maturation sporangia burst?
Select the correct statements for the process of budding in yeast:
I. A bud arises from a particular region on a parent body.
II. A parent cell divides into two daughter cells, here the parental identity is lost.
III. Before detaching from the parent body a bud may form another bud.
IV. A bud when detaches from the parent body grows into a new individual.
(A) I, II and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and I
(D) IV, I and II
A blue colour flower plant denoted by BB is crossbred with that of white colour flower plant denoted by bb.
(a) State the colour of flower you would expect in their F1 generation plants.
(b) What must be the percentage of white flower plants in F2 generation if flowers of F1 plants are self-pollinated?
(c) State the expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny.
After viewing different slides, a student draws following diagrams. Select the one which depicts binary fission in Amoeba:
 (A) a
(A) a
(B) b
(C) c
(D) d
Write a short note on regeneration.
Define vegetative propagation. List its two methods.
How is vegetative propagation economically important?
Grafting is not possible in the monocots because they
Name any one plant in which double fertilization was discovered?
Which of the following is not a type of asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms?
Seeds are the product of asexual reproduction.
A feature of reproduction that is common to Amoeba, Yeast, and Spirogyra is that ______
The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called ______
Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between
Mustard was growing in two fields- A and B. While Field A produced brown coloured seeds, field B produced yellow coloured seeds.
It was observed that in field A, the offsprings showed only the parental trait for consecutive generations, whereas in field B, majority of the offsprings showed a variation in the progeny.
What are the probable reasons for these?
Rajesh observed a patch of greenish black powdery mass on a stale piece of bread.
Name its vegetative and reproductive parts.
Match the columns:
| Column A (Asexual) | Column B (Examples) | ||
| (a) | Spore formation | (1) | Spirogyra |
| (b) | Conidia formation | (2) | Yeast |
| (c) | Fragmentation | (3) | Chlamydomonas |
| (d) | Budding | (4) | Penicillium |
Suppose there is one member of a particular kind of organism in a culture dish, which doubles itself in one hour through asexual reproduction. Work out the number of members of that kind of organism which will be present in the culture dish after ten hours. Such a colony of individuals arising from one parent is called a “clone”.
