Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Pollen grains are formed by _________ division in locules of anthers.
विकल्प
meiosis
mitosis
amitosis
binary
उत्तर
Pollen grains are formed by meiosis division in locules of anthers.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
What is pollination? Explain the different types of pollination.
In the following diagram showing the structure of embryo of a dicot seed, what are the parts marked I, II and III sequentially?
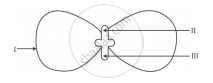
A student identified the various parts of an embryo of a gram seed and listed them as given below :
(I) Testa
(II) Plumule
(III) Radicle
(IV) Cotyledon
(V) Tegmen
Out of these the actual parts of the embryo are :
(A) I, II, III
(B) II, III, IV
(C) III, IV, V
(D) II, IV, V
Give one example of a unisexual flower.
The process of fusion of the male and female gametes is called ______.
Name the part made up of the stigma, style and ovary.
Name the swollen lower part of the carpel.
What is the function of a flower?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The male organ of reproduction in the flower is the.......... .
Explain the terms 'cross-pollination'?
How do the insects help in cross-pollination?
How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Explain the term 'fertilisation'.
Name the part of a seed which grows into root.
In what ways is fertilisation in a plant different from fertilisation in a human?
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Stamens make egg cells.
Find the odd-one out, giving reason:
Anther, pollen grain, ovule male gamete
What are the male and female gametes in a flowering plant?
Give one example each of unisexual and bisexual flowers. Differentiate between the two types of pollination that occur in flowers. What happens when a pollen lands on a suitable stigma? Write about the events that occur till the seed formation in the ovary.
In the figure, the parts marked A, B and C are sequentially:

(A) Plumule, Radicle and Cotyledon
(B) Radicle, Plumule and Cotyledon
(C) Plumule, Cotyledon and Radicle
(D) Radicle, Cotyledon and Plumule
Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each. Draw a diagram showing process of germination of pollen grains on stigma and label the following parts:
(a) Female germ cell
(b) Male germ cell
(c) Ovary
Write the names of male and female reproductive parts of a flower.
Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism.
Which of the following is not an unisexual flower?
a) Coconut
b) Papaya
c) Gulmohor
d) Maize
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Flower with its sexual reproductive organs
A student is observing the temporary mount of a leaf peel under a microscope. Draw a labelled diagram of the structure of stomata as seen under the microscope
Differentiate between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Find the odd one out:
Accessory whorls : Calyx and corolla : : essential whorls : ______________
Give scientific reason.
Fertilization in plants is called double fertilization.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Double fertilization in angiosperms
Write the events involved in the sexual reproduction of a flowering plant.
a. Discuss the first event and write the types.
b. Mention the advantages and the disadvantages of that event.
Generally, in a pollen tube, which of the following moves to the tip of the tube?
What would be the number of chromosomes in the cells of the aleurone layer in a plant species with 8 chromosomes in its synergids?
Which out of the following processes does not lead to the formation of clones.
In a bisexual flower inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
What is the structural unit of sexual reproduction in plant?
In flowering plants, the pollen grains are transferred to stigma by pollination but the female germ cells are present in the ovary.
Explain with the help of a labelled diagram (only concerned parts), how the male germ cell reaches the ovary.
