Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain with an example the inheritance of the dihybrid cross. How is it different from monohybrid cross?
उत्तर
The dihybrid cross involves the inheritance of two pairs of contrast characteristics, round–yellow seeds and wrinkled–green seeds. When pea plants having round – yellow seeds cross-bred with pea plants having wrinkled – green seeds, in the first generation (F1), only round yellow seeds were produced.
No wrinkled–green seeds were obtained. Round yellow colour seeds were dominant and wrinkled-green seeds were recessive.
When round–yellow seeds were cross-bred by self-pollination, four types of seeds having different combinations of shape and colour were obtained in the F2 generation. They were round- yellow, round-green, wrinkled-yellow, and wrinkled – green seeds.

Parents (P) Parental gametes First generation (F1)
Round, Yellow - 9 Wrinkled, Yellow - 3
Round, Green - 3 Wrinkled, Green - 1
Second generation (F2)
Dihybrid Cross
A dihybrid cross produced four types of F2 offsprings in the ratio of 9 with two dominant traits, 3 with one dominant trait and one recessive trait, 3 with another dominant trait and another recessive trait and one with two recessive traits. The new combinations of traits with round green and wrinkled yellow had appeared in the dihybrid cross (F2 generation). The ratio of each phenotype of seeds in the F2 generation is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. This is known as the Dihybrid ratio.
Difference between a monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross:
Monohybrid cross:
A Monohybrid cross is a genetic cross, that involves a single pair of genes, which is responsible for one trait.
Parents differ by a single trait.
The Monohybrid ratio in F2 generation is 3 : 1.
Dihybrid cross:
Dihybrid cross is a genetic cross, that involves two pairs of genes, which are responsible for two traits,
The parents have two different independent traits.
The dihybrid ratio in the F2 generation is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Filling the blank based on the given relationship.
3 : 1 Monohybrid : : 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 : ______
A homozygous Tall plant (T) bearing red coloured (R) flowers is crossed with a homozygous dwarf plant (t) bearing white flowers (r):
(1) Give the Genotype and Phenotype of the F2 generation.
(2) Give the possible combinations of the gametes that can be obtained from the F2 hybrid.
(3) Give the dihybrid ratio and the phenotype of the offsprings of the F2 generation when two plants of the F1 generation above are crossed.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
A character that is suppressed is _________.
Multiple Choice Question
When two individuals differing in at least one character are crossed, the process is known as:
The physical expression of a gene is called ______.
In a test cross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental type offspring were produced than the recombination type offspring. This indicates
Name the seven contrasting traits of Mendel.
Findings of Gregor Mendel were rediscovered by the following scientists EXCEPT for ______
In a testcross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant-type offspring. This indicates ______.
Two linked genes a and b show 20% recombination. The individuals of a dihybrid cross between ++ /++ × ab/ab shall show gametes ______.
A dihybrid condition is ______.
The process of mating between closely related individuals is ______.
In a dihybrid cross, F2 phenotypic ratio is 13 : 3. It is case of ______.
Given below is a dihybrid cross performed on Drosophila.
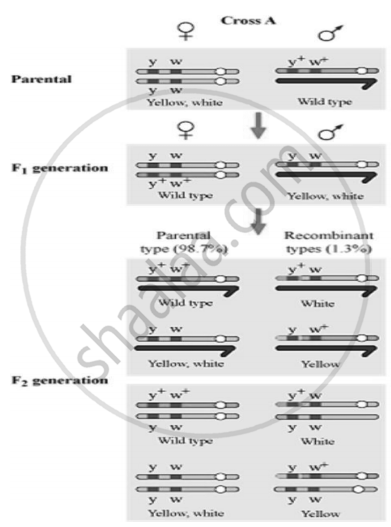
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn on the basis of this cross? When yellow bodied (y), white-eyed (w) Drosophila females were hybridized with brown bodied (y+), red-eyed males (w+) and F1 progenies were intercrossed, F2 generation would have shown the following ratio:
What is the difference between genetic drift and change due to natural selection?
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
What will be set of genes present in the F1 generation?
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
When F1 plants were self-pollinated, a total of 800 plants were produced. How many of these would be tall, medium height or short plants? Give the genotype of F2 generation.
Independent assortment means:
