Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure below shows a metal rod AB placed on an insulating stand.
In figure (a) a negatively charged ebonite rod C is touched with the metal rod AB, while in figure (b), the negatively charged ebonite rod C is held near the rod AB. State the kind of charges at the ends A and B of the rod, in each case.
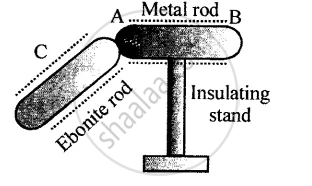
उत्तर
Explanation of Charges:
Case (a): The negatively charged ebonite rod C touches the metal rod AB
- When the ebonite rod C (negatively charged) touches the metal rod AB, electrons are transferred from the ebonite rod to the metal rod because metals are good conductors.
- Charges at the ends:
- End A: Negatively charged (electrons transferred from the ebonite rod).
- End B: Negatively charged (charge spreads evenly across the metal rod).
Case (b): The negatively charged ebonite rod C is held near the rod AB (without touching it)
- In this case, the induction process occurs:
- The negatively charged ebonite rod repels the free electrons in the metal rod AB, causing them to move to the far end (B).
- The end near the ebonite rod (A) becomes positively charged due to the deficiency of electrons.
- The far end (B) becomes negatively charged due to the accumulation of electrons.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Match the following
| Column A | Column B |
| Electric power | volt |
| kWh | joule |
| Electric current | volt × ampere |
| Electric energy | watt |
| watt | ampere |
| potential difference | electrical energy |
Charge is shared in charging a conductor by the method of ...............
Two objects when rubbed together get charged. The charges on them are
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, the glass rod and the silk get charged because
The rod in a gold leaf electroscope is made up of
What do you mean by conservation of charges?
An ebonite rod is rubbed with fur. Compare the charges acquired by them.
What causes the charging of two objects when they are rubbed together?
An ebonite rod is rubbed with fur. Explain the charging of the ebonite rod and the fur on the basis of electron movement.
A negatively charged ebonite rod is touched with the disc of a negatively charged gold leaf electroscope. What will be your observation?
