Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 1.02 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, very high resistance of 600 kΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf ε and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire.
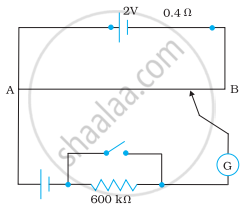
(a) What is the value ε?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of 600 kΩ have?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Is the balance point affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell?
(e) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V?
(f) Would the circuit work well for determining an extremely small emf, say of the order of a few mV (such as the typical emf of a thermo-couple)? If not, how will you modify the circuit?
उत्तर
(a) Constant emf of the given standard cell, E1 = 1.02 V
Balance point on the wire, l1 = 67.3 cm
A cell of unknown emf, ε, replaced the standard cell. Therefore, new balance point on the wire, l = 82.3 cm
The relation connecting emf and balance point is,
`"E"_1/"l"_1 = ε/"l"`
ε = `"l"/"l"_1 xx "E"_1`
= `82.3/67.3 xx 1.02`
= 1.247 V
The value of unknown emf is 1.247 V.
(b) The purpose of using the high resistance of 600 kΩ is to reduce the current through the galvanometer when the movable contact is far from the balance point.
(c) The balance point is not affected by the presence of high resistance.
(d) The point is not affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell.
(e) The method would not work if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V. This is because if the emf of the driver cell of the potentiometer is less than the emf of the other cell, then there would be no balance point on the wire.
(f) The circuit would not work well for determining an extremely small emf. As the circuit would be unstable, the balance point would be close to ending A. Hence, there would be a large percentage of errors.
The given circuit can be modified if a series resistance is connected with the wire AB. The potential drop across AB is slightly greater than the emf measured. The percentage error would be small.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
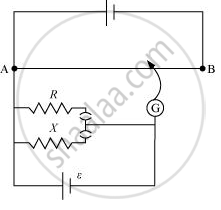
Figure 3.34 shows a potentiometer circuit for comparison of two resistances. The balance point with a standard resistor R = 10.0 Ω is found to be 58.3 cm, while that with the unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What might you do if you failed to find a balance point with the given cell of emf ε?
State the underlying principle of a potentiometer ?
When a resistor of 5Ω is connected across the cell, its terminal potential difference is balanced by 150 cm of potentiometer wire and when a resistance of 10 Ω is connected across the cell, the terminal potential difference is balanced by 175 cm same potentiometer wire. Find the balancing length when the cell is in open circuit and the internal resistance of the cell.
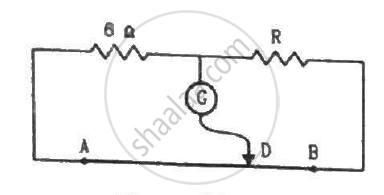
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 50 cm long. When AD = 30 cm, no deflection occurs in the galvanometer. Find R.
When the balance point is obtained in the potentiometer, a current is drawn from ______.
What is the SI unit of potential gradient?
The potentiometer is more sensitive, when ______.
Two cells when connected in series are balanced on 8 m on a potentiometer. If the cells are connected with polarities of one of the cell reversed, they balance on 2 m. The ratio of e.m.f's of the two cells is ____________.
When two cells of e.m.f 1.5 V and 1.1 V connected in series are balanced on a potentiometer, the balancing length is 260 cm. The balancing length, when they are connected in opposition is (in cm) ____________.
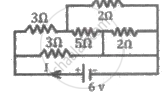
The current drawn from the battery in the given network is ______
(Internal resistance of the battery is neglected)
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
A potentiometer wire of length 'L' and a resistance 'r' are connected in series with a battery of E.M.F. 'E0' and a resistance 'r1'. A cell of unknown E.M.F, 'E' is balanced at a length 'ℓ' of the potentiometer wire. The unknown E.M.F. E is given by ______
In the experiment of potentiometer, at balance point, there is no current in the ______.
In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the 7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should ______.
Two cells of same emf but different internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in series with a resistance R. The value of resistance R, for which the potential difference across second cell is zero, is ______.
What is the value of resistance for an ideal voltmeter?
What should be the diameter of a soap bubble such that the excess pressure inside it is 51.2 Pa? [Surface tension of soap solution = 3.2 × 10−2 N/m]
