Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A biconvex lens with its two faces of equal radius of curvature R is made of a transparent medium of refractive index μ1. It is kept in contact with a medium of refractive index μ2 as shown in the figure.
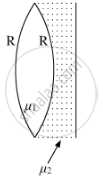
(a) Find the equivalent focal length of the combination.
(b) Obtain the condition when this combination acts as a diverging lens.
(c) Draw the ray diagram for the case μ1 > (μ2 + 1) / 2, when the object is kept far away from the lens. Point out the nature of the image formed by the system.
उत्तर
From the lens maker formula, we have
`1/f=(μ−1)(1/R_1−1/R_2)`
where f=Focal length the lens
μ=Refractive index of material
R1=Radius of curvature of first face
R2=Radius of curvature of second face
Let f1 anf f2 be the focal lengths of the two mediums. Then,
`1/f_1=(μ_1−1)[1/R−(−1/R)]`
`⇒1/f=(μ_1−1)(2/R)1/f_2`
`=(μ_2−1)[(−1/R)−1/∞]`
`⇒1/f_2=(μ_2−1)(−1/R)`
(a) If feq is the equivalent focal length of the combination, then
`1/f_eq=1/f_1+1/f_2`
`⇒1/f_eq=(2(μ_1−1))/R−(μ_2−1)/R`
`⇒1/f_eq=(2μ_1−μ_2−1)/R`
`⇒f_eq=R/(2μ_1−μ_2−1)`
(b) For the combination to behave as a diverging lens, feq < 0
`⇒R/(2μ_1−μ_2−1)<0`
`⇒2μ_1−μ_2−1<0`
`⇒μ_1<(μ_2+1)/2`
which is the required condition
(c) For μ1>(μ2+1)/2, the combination will behave as the converging lens. So, an object placed far away from the lens will form image at the focus of the lens.
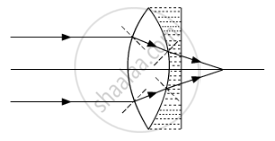
The image so formed will be real and diminished in nature.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A biconvex lens made of a transparent material of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water of refractive index 1.33. Will the lens behave as a converging or a diverging lens? Give reason.
name the factors on which 'limit of resolution' depends ?
The size of an object as perceived by an eye depends primarily on
To increase the angular magnification of a simple microscope, one should increase ______.
A simple microscope has a magnifying power of 3.0 when the image is formed at the near point (25 cm) of a normal eye. (a) What is its focal length? (b) What will be its magnifying power if the image is formed at infinity?
Find the maximum magnifying power of a compound microscope having a 25 diopter lens as the objective, a 5 diopter lens as the eyepiece and the separation 30 cm between the two lenses. The least distance for clear vision is 25 cm.
The angular magnification of a system is less than one. Does it mean that the image formed is inverted?
Why are the magnification properties of microscopes and telescopes defined in terms of the ratio of angles and not in terms of the ratio of sizes of objects and images?
A compound microscope has a magnifying power of 100 when the image is formed at infinity. The objective has a focal length of 0.5 cm and the tube length is 6.5 cm. Find the focal length of the eyepiece.
The focal length of the objective of a telescope is 60 cm. To obtain a magnification of 20, the focal length of the eye piece should be:
