Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the energy of photon which have momentum 2 × 10-16 gm-cm/sec.
उत्तर
Given, P = `2 × 10^(−16)` gm−cm/sec; c = 3 × 1010 cm/sec
E = pc
= 2 × 10−16 × 3 × 1010
= 6 × 10–6 erg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the photoelectric effect?
Using the values of work function given in the following table, tell which metal will require the highest frequency of incident radiation to generate photocurrent.
Typical values of work function for some common metals
| Metal | Work function (in eV) |
| Potassium | 2.3 |
| Sodium | 2.4 |
| Calcium | 2.9 |
| Zinc | 3.6 |
| Silver | 4.3 |
| Aluminium | 4.3 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| Copper | 4.7 |
| Nickel | 5.0 |
| Gold | 5.1 |
Radiation of wavelength 4500 Å is incident on a metal having work function 2.0 eV. Due to the presence of a magnetic field B, the most energetic photoelectrons emitted in a direction perpendicular to the field move along a circular path of radius 20 cm. What is the value of the magnetic field B?
Planck's constant is 6.6 × 10-34 Js. The momentum of each photon is given radiation Is 3.3 × 10-29 kg/s. The λ of radiation is ______.
Explain the concept of the photoelectric effect.
State Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain all characteristics of the photoelectric effect, on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
The maximum velocity of photoelectron emitted is 4.8 m/s. If the e/m ratio of the electron is 1.76 × 1011 C/kg, then stopping potential is given by ______
The kinetic energy of the most energetic photoelectron emitted from a metal surface is doubled when the wavelength of the incident radiation is reduced from λ1 to λ2. The work function of the metal is ______
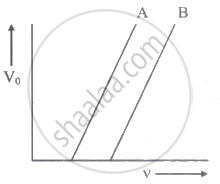
The following graph shows the stopping potential V0 versus frequency v for photoelectric emission from two metals A and B. The slope of each of the lines gives ______
When a light of wavelength 4000 Å falls on a photoelectric emitter, photoelectrons are liberated. For another emitter, light of wavelength 6000 Å is sufficient for photo emission. The work functions of the two emitters are in the ratio of ____________.
The work function of a metal is 1.6 x 10-19 J. When the metal surface is illuminated by the light of wavelength 6400 Å, then the maximum kinetic energy of emitted photo-electrons will be (Planck's constant h = 6.4 x 10-34 Js) ____________.
Photoelectrons emitted from a metallic surface are initially ____________.
In photoelectric effect, graph of saturation current versus frequency of light is plotted. The nature of the graph will be ____________.
When wavelength of incident radiation on the metal surface is reduced from 'λ1' to 'λ2', the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons is tripled. The work function of the metal is ______.
(h = Planck's constant, c =velocity of light)
Light of different frequencies, whose photons have energies 3 eV and 18 eV respectively, successively illuminate a metal of work function 2 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons will be ______.
Following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (F) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph (v0 = Threshold frequency).
The work function of a photosensitive material is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photon emission from the substance is (approximately) ____________.
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength '`lambda`', the stopping potential for photoelectric effect is '3V0'. If the same surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength '`2 lambda`', the stopping potential is found as 'V0'. The threshold wavelength for this surface is ____________.
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If the photoelectrons emitted from this surface have the de-Broglie wavelength '`lambda_1`' then ____________.
In experiment of photoelectric effect, the stopping potential for incident yellow light of wavelength 5890 Å is 4 volt. If the yellow light is replaced by blue light of wavelength 4000 Å, the stopping potential is ____________.
The radiation corresponding to the 3 → 2 transition of a hydrogen atom falls on a gold surface to generate photoelectrons. These electrons are passed through a magnetic field of 5 × 10-4 T. Assume that the radius of the largest circular path followed by these electrons is 7 mm, and the work function of the metal is ______.
(Mass of electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg)
When radiation of wavelength λ is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the stopping potential is V. When the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is `"V"/4`. If the threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is nλ. then value of n will be ______.
Photoelectrons are observed to just emit out of a material surface when the light of 620 nm falls on it with the intensity of 100 W m-2. If the light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the same material with an intensity of 1 W m-2, what would be the minimum reverse potential needed to stop the outflow of the electrons?
The wavelength of light incident on a metal surface is reduced from 300 nm to 200 nm (both are less than threshold wavelength). What is the change in the stopping potential for photoelectrons emitted from the surface will be ______ V. (Take h = 6.6 × 10-34 J-s)
A charged dust particle of radius 5 × 10-7 m is located in a horizontal electric field having an intensity of 6.28 × 105 V/m. The surrounding medium is air with a coefficient of viscosity η = 1.6 × 10-5 N-s/m2. If the particle moves with a uniform horizontal speed of 0.02 m/s, the number of electrons on it is ______.
Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1.3 eV and 2.8 eV respectively, successfully illuminate a metallic surface whose work function is 0.8 eV. The ratio of maximum speeds of emitted electrons will be ______.
Define photoelectric work function of a metal.
The threshold frequency for a certain metal for photoelectric effect is 1.7 x 1015 Hz. When a light of frequency 2.2 x 1015 Hz is incident on the metal surface, the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is 3.3 x.10-19 J. Calculate Planck's constant.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
