Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For any arbitrary motion in space, state whether the following statement is true:
`"V"_"average"` = [r(t2) - r(t1) ] /(t2 – t1)
पर्याय
True
False
उत्तर
This statement is True.
Explanation:
This equation can represent the particle's arbitrary motion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
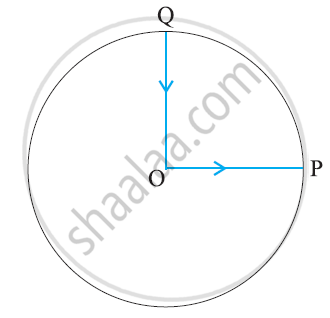
A cyclist starts from the centre O of a circular park of radius 1 km, reaches the edge P of the park, then cycles along the circumference, and returns to the centre along QO as shown in figure. If the round trip takes 10 min, what is the (a) net displacement, (b) average velocity, and (c) average speed of the cyclist?
In a harbour, wind is blowing at the speed of 72 km/h and the flag on the mast of a boat anchored in the harbour flutters along the N-E direction. If the boat starts moving at a speed of 51 km/h to the north, what is the direction of the flag on the mast of the boat?
For any arbitrary motion in space, state whether the following statement is true:
`"a"_"average"=["v"("t"_2) - "v"("t"_1)]/("t"_2 - "t"_1)`
(The ‘average’ stands for average of the quantity over the time interval t1 to t2)
In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v0 is a positive constant. Then, which of the following are necessarily true?
In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v0 is a positive constant. Then which of the following are necessarily true?
In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v0 is a positive constant. Then which of the following are necessarily true?
Motion in two dimensions, in a plane can be studied by expressing position, velocity and acceleration as vectors in cartesian co-ordinates A = `A_xhati + A_yhatj` where `hati` and `hatj` are unit vector along x and y directions, respectively and Ax and Ay are corresponding components of (Figure). Motion can also be studied by expressing vectors in circular polar co-ordinates as A = `A_rhatr + A_θhatθ` where `hatr = r/r = cos θhati + sin θj` and `hatθ = - sin θhati + cos θ hatj` are unit vectors along direction in which `r` and `θ` are increasing.
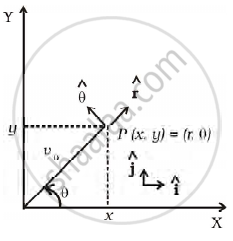
- Express `hati` and `hatj` in terms of `hatr` and `hatθ`
- Show that both `hatr` and `hatθ` are unit vectors and are perpendicular to each other.
- Show that `d/(dt) (hatr) = ωhatθ` where `θ = (dθ)/(dt)` and `d/(dt) (hatθ) = - ωhatr`
- For a particle moving along a spiral given by `t = aθhatr`, where a = 1 (unit), find dimensions of ‘a’.
- Find velocity and acceleration in polar vector representation for particle moving along spiral described in (d) above.
A small toy starts moving from the position of rest under constant acceleration. If it travels a distance of 10 minutes, the distance travelled by the toy in the next will be ______.
The position of a particle is x - y plane is described by the variables x = at3 and y = 2at. Then the acceleration of the particle ______.
A particle of mass 10-2 kg is moving along the positive x-axis under the influence of a force F(x) = `-"K"/(2x)^2` where K = 10-2 Nm2. At time t = 0 it is at x = 1.0 m and its velocity is v = 0. The velocity of particle will be ______ m/s, when it reaches x = 0.50 m.
