Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
उत्तर १
For a reaction, A + B⟶ P
Rate1 = k[A][B]2
If the concentration of B is doubled
Rate2 = k[A][2B]2
Rate1 = k[A][B]2
Rate2 = k[A][2B]2
Rate1 = B2
Rate2 4B2
Rate2 = 4 Rate1
The rate of reaction will be four times the initial rate.
उत्तर २
A + B → P
Rate = k[A] [B]2
Since the given reaction has order two with respect to reactant B, thus, if the concentration of B is doubled in the given reaction, then the rate of reaction will become four times.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A → B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 × 10-5m-s-1. When [A] is 0.6m, rate constant of the reaction is
- 1.1 × 10-5s-1
- 1.1 × 10-4s-1
- 9 × 10-5s-1
- 9 × 10-4s-1
For a reaction : 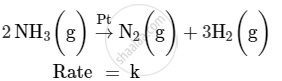
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the following results were obtained :
| t/s | 0 | 30 | 60 |
| [CH3COOCH3] / mol L–1 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
(i) Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains constant.
(ii) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
For a reaction, \[\ce{A + B -> Product}\]; the rate law is given by, `r = k[A]^(1/2)[B]^2`. What is the order of the reaction?
Molecularity of a reaction _____________.
Consider the reaction A ⇌ B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
A catalyst in a reaction changes which of the following?
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
For a chemical reaction starting with some initial concentration of reactant At as a function of time (t) is given by the equation,
`1/("A"_"t"^4) = 2 + 1.5 xx 10^-3` t
The rate of disappearance of [A] is ____ × 10-2 M/sec when [A] = 2 M.
[Given: [At] in M and t in sec.]
[Express your answer in terms of 10-2 M /s]
[Round off your answer if required]
Assertion (A): Order of reaction is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions.
Reason (R): For a complex reaction, molecularity has no meaning.
