Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
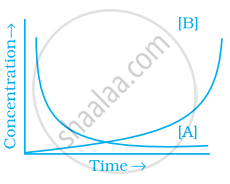
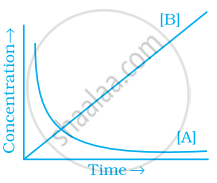
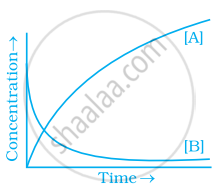
Consider the reaction A ⇌ B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
पर्याय
उत्तर
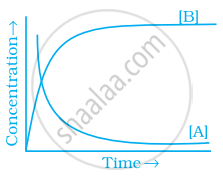
Explanation:
If \[\ce{A -> B}\] then the concentration of both reactants and the products very exponentially with time. But graph the reactant concentration decreases exponentially and the product concentration increases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a first order reaction x → y, 40% of the given sample of compound remains unreacted in 45 minutes. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
| Experiment | Time/s–1 | Total pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010)
From the rate expression for the following reaction, determine the order of reaction and the dimension of the rate constant.
\[\ce{H2O2_{( aq)} + 3I^-_{( aq)} + 2H^+ -> 2H2O_{(l)} + I^-_3}\] Rate = k[H2O2][I−]
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below :
\[\ce{A(g) -> B(g) + C(g)}\]
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’ The rate constant k for the reaction is given as ______.
In any unimolecular reaction:
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
The role of a catalyst is to change
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction.
For a reaction R → p the concentration of reactant change from 0.03 m to 0.02 m in minute, calculate the average rate of the reaction using the unit of second.
Identify the order of reaction from the following unit for its rate constant:
L mol–1s–1