Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the circuit shown in the diagram below:

What is the value of:
(i) current through 6 Ω resistor?
(ii) potential difference across 12 Ω resistor?
उत्तर
The resistors of 6 Ω and 3 Ω are connected in series. Therefore, their net resistance can be calculated as:
R = R1 + R2
Here, R1 = 6 Ω
R2 = 3 Ω
So:
R = 6 Ω + 3 Ω = 9 Ω
The current through this branch, I = V/R
I = 4/9 = 0.44 A
In a series combination, the current remains the same. So the current through the 6 Ω resistor is 0.44 A.
(2) The current through the branch with resistors of 12 Ω and 3 Ω:
I = V/R
I = 4/(12 + 3) = 4 / 15 A
The potential difference across the 12 Ω resistance can be obtained by using the equation,
V = IR.
V = (4 / 15) x 12 = 3.2 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State whether the resistivity of a wire changes with the change in the thickness of the wire.
Calculate the work done in moving a charge of 4 coulombs from a point at 220 volts to another point at 230 volts.
What is Ohm's law? Explain how it is used to define the unit of resistance.
A current of 1.6 mA flows through a conductor. If charge on an electron is –1.6 × 10-19 coulomb, find the number of electrons that will pass each second through the cross section of that conductor.
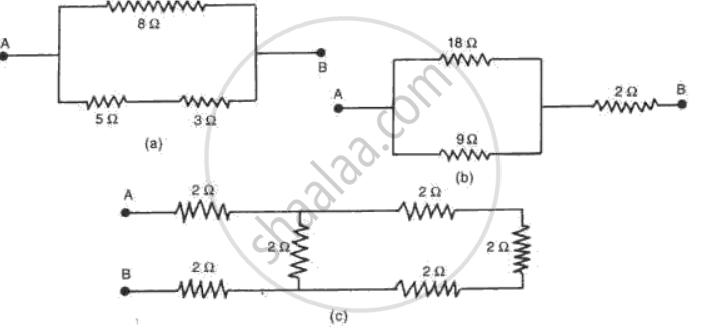
What is the combined resistance of each of the networks between A and B shown in fig. ?
If P and V are the power and potential of device, the power consumed with a supply potential V1 is:
A cylindrical conductor of length l and uniform area of cross section A has resistance R. Another conductor of length 2l and resistance R of the same material has area of cross section
Define Electric potential.
A negative charge will move from ______ to ______ potential.
Study the following circuit and find:

- Effective resistance of the circuit
- Current drawn from the battery
- Potential difference across the 5 omega resistor
