Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give an account of one Mendelian and one chromosomal disorder you have studied.
उत्तर
Mendelian disorders are mainly caused due to alteration or mutation in the gene. e.g. Thalassemia, sickle cell anaemia, colour blindness, haemophilia, phenylketonuria, etc.
- Thalassemia
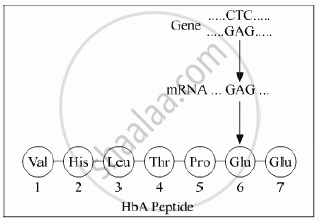
- Thalassemia is an autosomal, inherited recessive disease.
- A hemoglobin molecule is made of four polypeptide chains- 2 alpha (a) and 2 betas (b) chains.
- The synthesis of alpha chains is controlled by two closely linked genes (HBA1 and HBA2) on chromosome 16 while the synthesis of the beta chain is controlled by a single gene (HBB) on chromosome 11.
- Depending upon which chain of hemoglobin is affected, thalassemia is classified as alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia.
- It is caused due to deletion or mutation of a gene that codes for alpha (α) and beta (β) globin chains that result in the abnormal synthesis of hemoglobin.
- In Thalassemia, the person shows symptoms like anaemia, pale yellow skin, change in size and shape of RBCs, slow growth and development, dark urine, etc.
- Chromosomal Disorders are caused due to the absence or excess of one or more chromosomes or their abnormal arrangement. e.g. Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, etc.
- Turner Syndrome (X monosomy / XO females):
1. It is a sex chromosomal disorder caused due to non-disjunction of chromosome during gamete formation.
2. Individual born with Turner syndrome has 44 autosomes with XO.
3. They are phenotypically female. They have short stature (height) and webbed neck, lower posterior hairline, broad shield-shaped chest, poorly developed ovaries, and breast, and low intelligence. - Klinefelter syndrome (XXY males):
1. It is chromosomal disorder caused due to an extra X chromosome in males. Thus genotype of individuals is 44 + XXY. They are described as feminized males.
2. Extra chromosome is a result of non-disjunction of X-chromosome during meiosis.
3. Individual is male and has overall masculine development.
4. Individuals have harsh voice pitches and underdeveloped testis.
5. They are tall with long arms, feminine development (development of breast i.e. Gynaecomastia), and spermatogenesis does not occur, therefore, individuals are sterile. - Down syndrome:
1. Individuals suffering from Down syndrome will have 47 chromosomes instead of the normal number 46.
2. 21st Trisomy occurs due to non-disjunction or failure of separation of chromosomes (autosomes) during gamete formation.
3. Following are the symptoms of Down syndrome:
- Mild or moderate mental retardation and poor skeletal development.
- Distinct facial features like small head, ears, and mouth.
- The face is typically flat and rounded with a flat nose, open mouth, and protruding tongue.
- Eyes slant up and out with internal epicanthal folds.
- Flat hands and stubby fingers, the palm is broad with a single palmer crease.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given below is the representation of amino acid composition not the relevant translated portion of β-chain of haemoglobin, related to the shape of human red blood cells
(a) Is this representation indicating a normal human or a sufferer from certain related genetic disease? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) What difference would be noticed in the phenotype of the normal and the sufferer related to this gene?
(c) Who are likely to suffer more from the defect related to the gene represented the males, the females or both males and females equally? And why?
Give an example of an autosomal recessive trait in humans. Explain its pattern of inheritance with the help of a cross.
A male rabbit of genotype 'AABBDDEE' is crossed with a female rabbit of genotype 'aabbddee' to produce F1 hybrid offspring. How many genetically different gametes can be produced by this F1 hybrid?
Match the Column I and Column II and select the correct option.
| List-I | List-II | ||
| i. | Holandric genes | a. | Pleiotropy |
| ii. | Multiple effects of a single gene | b. | Hypertrichosis |
| iii. | Skin colour in man | c. | Multiple Alleles |
| iv. | ABO Blood types | d. | Polygenic inheritance |
The correct answer is
Identify the characteristics that are observed in an individual suffering from Klinefelter syndrome.
i. Gynaecomastia, under developed testis and no spermatogenesis.
ii. Voice pitch is harsh.
iii. They are tall with long arms.
Select the incorrect statement regarding pedigree analysis.
Mongolism is a genetic disorder which is caused by the presence of an extra chromosome number ______.
Read the following and answer from given below:
According to Mendel, one gene controls the expression of one character only. The ability of a gene to have multiple phenotypic effects because it influences a number of characters are an exception. The gene has multiple phenotypic effects because its ability to control two or more characters can be seen in cotton. In cotton, a gene for the lint also influences the height of the plant, size of the ball, number of ovules, and viability of seeds.
Which of the following disorder is an example of genes with multiple phenotypic effects?
Clotting of blood is to ______.
If a father and son are both defective in red-green colour vision, is it likely that the son inherited the trait from his father? Comment.
