Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given ahead is a diagram of an experimental setup to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:

- Name the colour of dry cobalt chloride paper.
- Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
- Why are glass slides placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers?
- After about half an hour, what change, if any, would you expect to find in the cobalt chloride paper placed on the dorsal and ventral sides of the leaf? Give a reason to support your answer.
उत्तर
- The colour of dry cobalt chloride paper is blue.
- Because the experimental leaf has reticulate venation and has more stomatal holes on its underside, it is a dicot leaf. This causes more obvious transpiration.
- To keep the strips in place, glass slides are set on dried cobalt chloride sheets.
- About half an hour later, the cobalt chloride paper on the dorsal side should turn less pink or take more time to turn pink. By comparison, the ventral side paper will turn pink faster. This variation arises from the higher rate of transpiration resulting from more stomata on the ventral surface of a dicot leaf than on its dorsal surface.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the following:
Any two parts of a leaf which allow transpiration.
Given ahead is the diagram of an experimental set up to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:

Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
The apparatus shown in the following diagram is Garreau’s potometer designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again.
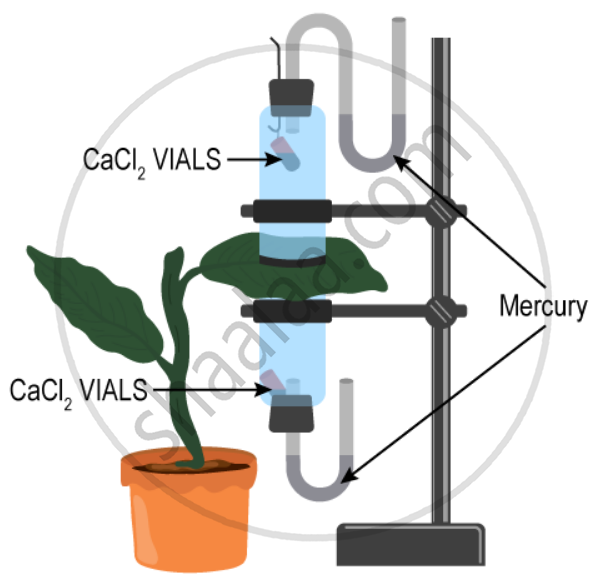
What is the purpose of using a manometer?
The diagram below represents a structure found in a leaf.
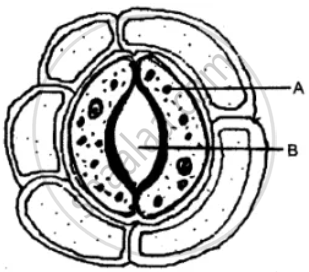
Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the pis labeled A and B.
(ii) What is the biological term for the above structure?
(iii) What is the function of the part labeled A?
(iv) Mention two structural features of A, which help in the function mentioned in (iii) above.
(v) Where is this structure likely to be found in a leaf?
(vi) The above structure helps in the process of transpiration. Explain the term transpiration.
(vii) How many other cells are found surrounding this structure as seen in the diagram?
Draw a neat diagram of the stomatal apparatus found in the epidermis of leaves and label the Stoma, Guard cells, Chloroplast, Epidermal Cells, cell wall and Nucleus.
Give Technical Term
Opening found on the undersurface of the dorsiventral leaf.
State the Location:
Stomata
Guard cells help in regulating the ______.
The paper used to demonstrate unequal transpiration in a dicot leaf is ______.
