Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given below is the diagram of an apparatus used to study a particular phenomenon in plants:
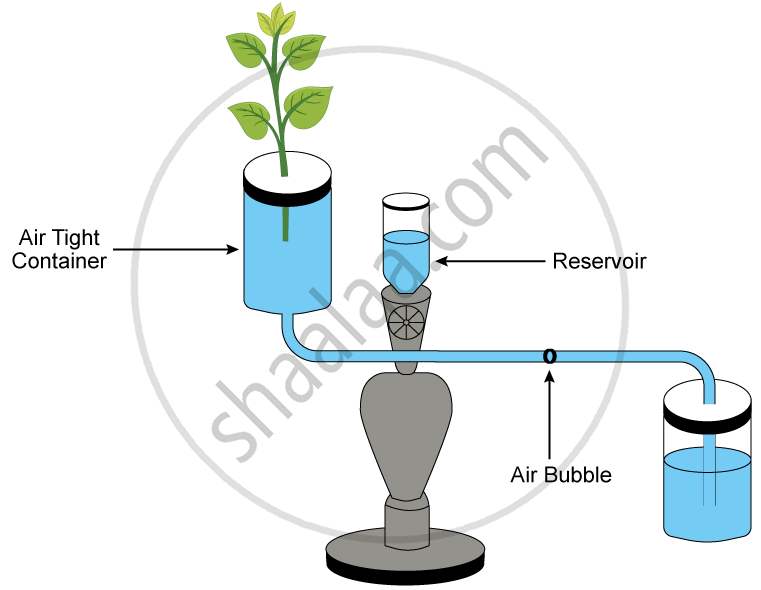
What happens to the movement of the air-bubble if the apparatus is kept:
(i) In the dark
(ii) In sunlight
(iii) In front of a fan
Give a reason in each case.
उत्तर
(i) If the apparatus is kept in the dark, there will be no transpiration as the stomata would be closed. As a result, there would be no movement of the air bubble and it would remain stable.
(ii) If the apparatus is kept in bright sunlight, the rate of transpiration will be more. As a result, the movement of the air bubble would be larger since there would be more loss of water due to transpiration.
(iii) If the apparatus is kept in front of a fan, the rate of transpiration will be more. As a result, the movement of the air bubble would be larger since there would be more loss of water due to transpiration as the velocity of wind/air increases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the following:
The apparatus to record the rate of transpiration in a cut shoot.
Which of the following statements are true and which ones are false? Give reason in support of your answer.
Forest contribute in bringing rains.
Which of the following statements are true and which ones are false? Give reason in support of your answer.
Potometer is an instrument used for Demonstration of transpiration occurring from the lower surface of a leaf.
What is a photometer?
What is lenticular transpiration? Mention one major difference between lenticular transpiration and stomatal transpiration.
Given below is the diagram of an apparatus used to study a particular phenomenon in plants:

- Name the apparatus.
- What is it used for?
- What is the role played by the air-bubble in this experiment?
- What is the use of the reservoir?
- What happens to the movement of the air-bubble if the apparatus is kept:
- in the dark
- in sunlight
- in front of a fan?
Give a reason in each case.
Given below is the diagram of an apparatus used to study a particular phenomenon in plants:
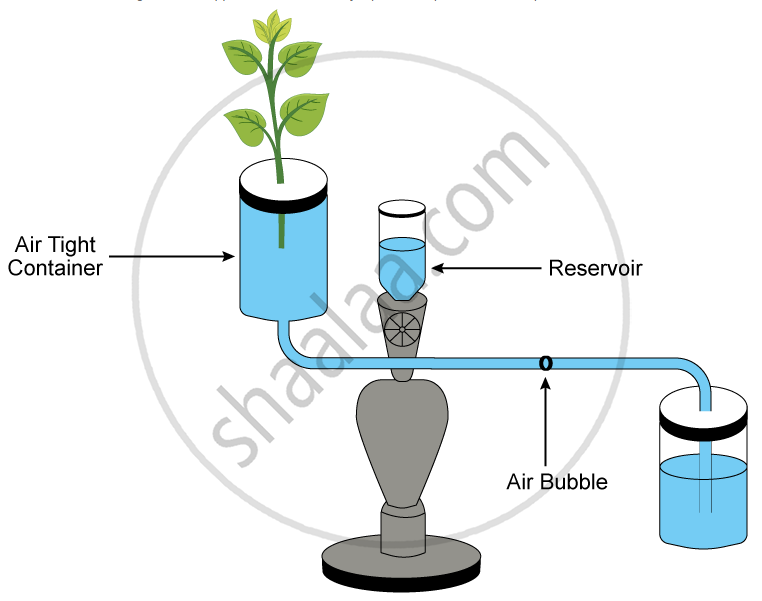
What is the use of the reservoir?
The apparatus shown in the following diagram is Garreau’s potometer designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again.
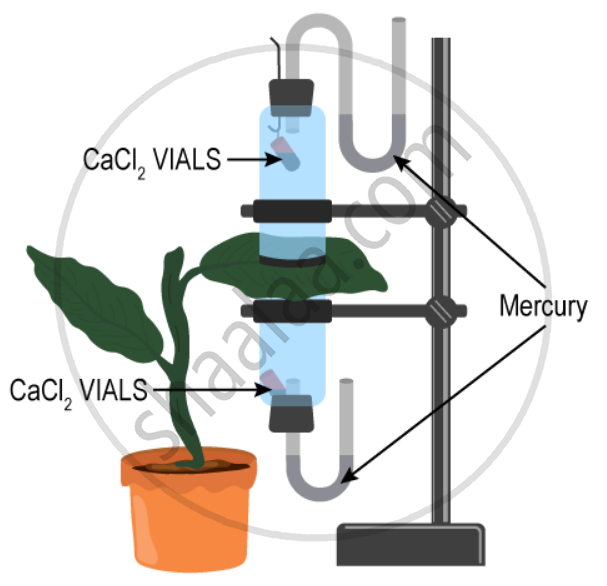
What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2 vials inside the cup?
The apparatus used to measure the rate of transpiration is ______.
Name four kinds of potometers on the basis of the names of the scientists who discovered them.
