Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of 6 Ω?
उत्तर
Equivalent resistance, R’ = 6 Ω
Consider the series combination of the resistors, as shown in the given circuit.
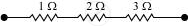
Equivalent resistance of the circuit is given by the sum,
R’ = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6 Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use Kirchhoff's rules to obtain conditions for the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge.
State Kirchhoff's rules and explain on what basis they are justified.
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/3) Ω?
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/5) Ω?
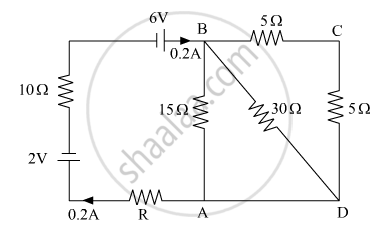
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points A and B?
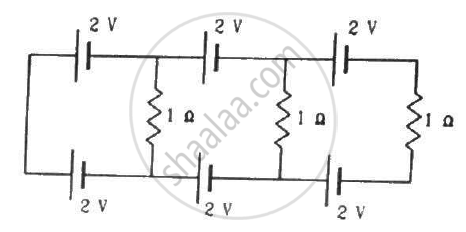
Find the circuit in the three resistors shown in the figure.
Twelve wires, each of equal resistance r, are joined to form a cube, as shown in the figure. Find the equivalent resistance between the diagonally-opposite points a and f.

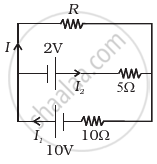
Two cells of voltage 10V and 2V and internal resistances 10Ω and 5Ω respectively, are connected in parallel with the positive end of 10V battery connected to negative pole of 2V battery (Figure). Find the effective voltage and effective resistance of the combination.
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in the analysis of electric circuits and explain them.
A 6-volt battery is connected to the terminals of a three-metre-long wire of uniform thickness and resistance of 100 ohms. The difference of potential between two points on the wire separated by a distance of 50 cm will be ______.
