Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Giving examples, differentiate between ‘roasting’ and ‘calcination’.
उत्तर
Roasting is the process of converting sulphide ores to oxides by heating the ores in a regular supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. For example, sulphide ores of Zn, Pb, and Cu are converted to their respective oxides by this process.

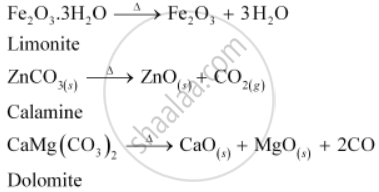
On the other hand, calcination is the process of converting hydroxide and carbonate ores to oxides by heating the ores either in the absence or in a limited supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. This process causes the escaping of volatile matter leaving behind the metal oxide. For example, hydroxide of Fe, carbonates of Zn, Ca, Mg are converted to their respective oxides by this process.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Out of C and CO, which is a better reducing agent for ZnO ?
The metal oxide which cannot be reduced to metal by carbon is ____________.
Which one of the following is not feasible
Flux is a substance which is used to convert
Zinc is obtained from ZnO by ____________.
What is the role of Limestone in the extraction of iron from its oxide Fe2O3?
Which reagents are required for one step conversion of chlorobenzene to toluene?
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ‘X’ while the of toluene with Cl2 in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus ‘X’ and ‘Y’are ______.
Extraction of gold and silver involves leaching the metal with CN– ion. The metal is recovered by ______.
Pb and Sn are extracted from their chief are by:-
CN– solution is used in the extraction of which metal?
Colemanite is:-
Sulphide ore of the metal are usually concentrated by froth floatation process. Which of the following sulphide ore offers an exception and is concentrated by chemical leaching?
Heating byrites to remove sulphtir is called
Heating pyrites to remove sulphur is called ______.
