Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Heterolytic fission of C–C bond results in the formation of ______.
पर्याय
free radical
Carbanion
Carbocation
Carbanion and Carbocation
उत्तर
Heterolytic fission of C–C bond results in the formation of carbanion and carbocation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For the following reactions
- \[\ce{CH3CH2CH2Br + KOH → CH3 – CH = CH2 + KBr + H2O}\]
- \[\ce{(CH3)3CBr + KOH → (CH3)3COH + KBr}\]
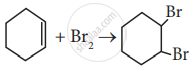
Which of the following statement is correct?
Which of the following species is not electrophilic in nature?
Homolytic fission of covalent bond leads to the formation of ______.
Which of the group has highest + I effect?
Assertion: Tertiary Carbocations are generally formed more easily than primary Carbocations ions.
Reason: Hyper conjucation as well as inductive effect due to additional alkyl group stabilize tertiary carbonium ions.
Which of the following species does not acts as a nucleophile?
What is electrophiles? Give a suitable example.
Explain inductive effect with suitable example.
Explain the electromeric effect.
Give example for the following type of organic reaction.
β - elimination
