Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How are electromagnetic waves produced?
उत्तर
Moving charges produce electric and magnetic field waves, which are then combined to form electromagnetic waves. All electromagnetic waves originate from charged particles. An electric field produced by this charged particle can act as a force on other adjacent charged particles. The charged particle produces a magnetic field and ripples or oscillations in its electric field as it accelerates as part of an oscillatory motion, as predicted by Maxwell's equations. Once a charged particle is in motion, the electric and magnetic fields it generates are self-replicating, with changes in either field (electric or magnetic) causing changes in the other. An electromagnetic wave's electric and magnetic fields will both vary over time, with one influencing the other. Any time a charged particle experiences a change in velocity, electromagnetic waves (photons) are generated. Energy is conserved via the electromagnetic wave (radiation) that is created when the charged particle changes its velocity. Light makes up this energy. Microwave oven manufacturing is a straightforward illustration of this. A magnetron is a part found within a microwave. A cavity that functions as an electron racecourse is located inside the magnetron. The electrons move extremely quickly over this little circular track. The electrons are moving back and forth towards the inside and outside of the racing track while they are moving at these extremely high speeds and in little circles. Microwaves are produced as a result of this high-frequency wriggling.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When Sunita, a class XII student, came to know that her parents are planning to rent out the top floor of their house to a mobile company she protested. She tried hard to convince her parents that this move would be a health hazard.
Ultimately her parents agreed :
(1) In what way can the setting up of transmission tower by a mobile company in a residential colony prove to be injurious to health?
(2) By objecting to this move of her parents, what value did Sunita display?
(3) Estimate the range of e.m. waves which can be transmitted by an antenna of height 20 m. (Given radius of the earth = 6400 km)
How does oscillating charge produce electromagnetic waves?
The energy levels of an atom of a certain element are shown in the given figure. Which one of the transitions A, B, C, D or E will result in the emission of photons of electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 618.75 nm? Support your answer with mathematical calculations.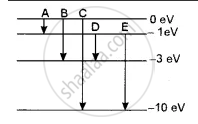
What are Fraunhofer lines? How are they useful in the identification of elements present in the Sun?
Write a short note on the X-ray.
A pulse of light of duration 10-6 s is absorbed completely by a small object initially at rest. If the power of the pulse is 60 x 10-3 W, calculate the final momentum of the object.
Which one of the following does not represent simple harmonic motion? Here y denotes the instantaneous displacement. Here, A and B are constants and co is the angular frequency.
A plane electromagnetic wave propagating along x direction can have the following pairs of E and B.
- Ex, By.
- Ey, Bz.
- Bx, Ey.
- Ex, By.
An infinitely long thin wire carrying a uniform linear static charge density λ is placed along the z-axis (figure). The wire is set into motion along its length with a uniform velocity `v = vhatk_z`. Calculate the poynting vector `S = 1/mu_0 (E xx B)`.
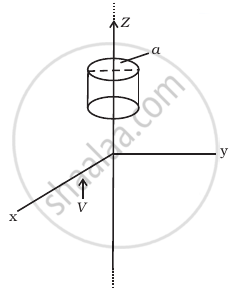
Write the two characteristics of electromagnetic waves.
