Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How are revenue receipts different from capital receipts in a budget? Give one example of each receipt.
उत्तर
| Revenue Receipts | Capital Receipts | |
| 1. | Revenue receipts are those receipts made by the government that do not incur any debt or reduce the government's assets. | Capital revenues are receipts that either increase liabilities or reduce the government's assets. |
| 2. | The government is under no obligation to refund the money. | The government is obligated to return the money plus interest. |
| 3. | It is a recurring in nature. | It is non-recurring in nature. |
| 4. | For example, income tax, GST (Goods and Services Tax), and so on. | For example, borrowing from the public, receipts from the sale of shares in a public sector company, and so on. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give reasons or Explain the following statements. (Any Three)
During the [eriod of depression deficit budgets is used.
Define or Explain.
Plan expenditure
Give reason of Explain the statement
Government revenue is more than government expenditure.
Distinguish between:
Revenue budget and capital budget
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement.
Capital budget consists of revenue receipts and revenue expenditure.
Answer in detail:
Explain capital receipts and capital expenditure as a part of Capital Budget.
Which of the following is a non-tax revenue?
One of the two components of government budget is ______.
One of the two components of the Revenue budget is ______.
One of the other two components of Capital budget is ______.
______ deals with how consumers or the producers make decisions depending on their given budget.
What are the objectives of budgetary policies?
Match the following
| A. | It does not create assets for the government | a. | fiscal deficit |
| B. | It results in the creation of assets. | b. | Revenue expenditure |
| C. | It is the excess of total expenditure over total receipts. | c. | Capital expenditure |
On the basis of the below-mentioned information answer the following question:
Net Receipt of the Centre (₹ in lakh crore)
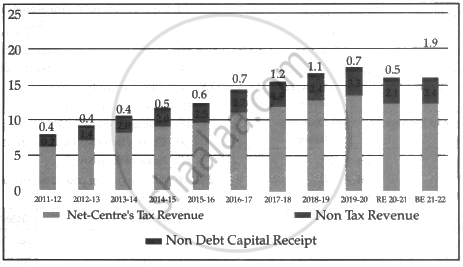
The value of non-tax revenue has ______ crores between 2016-17 and 2017-18.
Read the below case and answer the questions that follow:
The Centre on Saturday increased the budgetary allocation for the environment ministry from last fiscal by nearly five percent for 2020-21 with no change in the amount allotted to pollution abatement and climate change action plan. Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, allocated ₹3,100 crores for the ministry out of which ₹460 crores were allotted to control pollution, which is the same as the money it received in the last budget. Control of pollution has been conceptualized to provide financial assistance to Pollution Control Boards/Committees and funding to National Clean Air Programme (NCAP). Similarly, the budget for pollution abatement, which was cut by 50 percent last year from 2018-to 19, remained unchanged at ₹10 crores. The minister also announced that states, which are formulating and implementing plans for ensuring cleaner air in cities above one million population should be encouraged.
- Budget 2020: Allocation for Environment Ministry up 5% to ₹3,100 crore - Business Standards, 1st February 2020
What type of externality will the increase in budget allocation create?
