Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How can we explain the reddish appearance of sun at sunrise or sunset? Why does it not appear red at noon?
उत्तर
Light from the Sun near the horizon passes through thicker layers of air and larger distance in the earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. Near the horizon, most of the blue light and shorter wavelengths are scattered away by the particles. Therefore, the light that reaches our eyes is of longer wavelengths (reddish). This gives rise to the reddish appearance of the Sun.
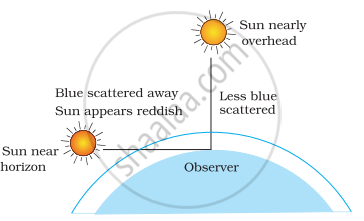
At noon, the Sun is nearly overhead, and hence the light would travel relatively shorter distance. At noon, the Sun appears white as only a little of the blue and violet colours are scattered.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of scattering of light, explain the reason for the difference in colours of the Sun as it appears during sunset/sunrise and noon.
What is a rainbow? Draw a labelled diagram to show the formation of a rainbow.
Which color of white light is scattered the least and why?
Give the meaning of the term VIBGYOR. With which phenomenon is it connected?
We can see the sun before the actual sunrise by about:
(a) 5 minutes
(b) 2 minutes
(c) 2 hours
(d) 20 minutes
What is the colour of the sunlight:
scattered by the dust particles in the atmosphere?
When sunlight enters the earth’s atmosphere, state which colour of light is scattered
- the most and
- which the least.
The clouds are seen white. Explain
Name the point on the lens through which a ray of light passes undeviated.
Describe an experiment to show that “sunlight is essential for photosynthesis”.
