Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How can we explain the reddish appearance of sun at sunrise or sunset? Why does it not appear red at noon?
Solution
Light from the Sun near the horizon passes through thicker layers of air and larger distance in the earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. Near the horizon, most of the blue light and shorter wavelengths are scattered away by the particles. Therefore, the light that reaches our eyes is of longer wavelengths (reddish). This gives rise to the reddish appearance of the Sun.
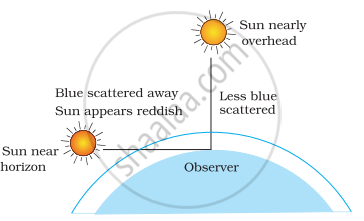
At noon, the Sun is nearly overhead, and hence the light would travel relatively shorter distance. At noon, the Sun appears white as only a little of the blue and violet colours are scattered.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Will this phenomenon be observed by an observer on the moon? Justify your answer with a reason.
Which color of white light is scattered the least and why?
Which colour of the spectrum has
longest wavelength,
Which colour of light has the shorter wavelength − red or violet?
Which phenomenon makes us see the sun:
a few minutes before actual sunrise?
We can see the sun before the actual sunrise by about:
(a) 5 minutes
(b) 2 minutes
(c) 2 hours
(d) 20 minutes
What happens when a beam of sunlight enters a dusty room through a window? Explain your answer.
In an experiment to study the scattering of light by passing a beam of white light through a colloidal solution of sulphur in a transparent glass tank:
Which colour is observed from the front of the glass tank? Does this colour correspond to the colour of sky on a clear day or the colour of sky around the sun at sunset?
The clouds are seen white. Explain
A beam of blue, green, and yellow light passes through the earth's atmosphere. Name the colour which is scattered the least.
