Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Acids, Bases and Salts
3: Metals and Non-metals
4: Carbon and its Compounds
5: Periodic Classification of Elements
6: Life Processes
7: Control and Coordination
8: How do Organisms Reproduce?
9: Heredity and Evolution
10: Light – Reflection and Refraction
▶ 11: The Human Eye and the Colourful World
12: Electricity
13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
14: Sources of Energy
15: Our Environment
16: Management of Natural Resources
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Science [English] Class 10.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 11 The Human Eye and the Colourful World Multiple Choice Questions [Pages 86 - 88]
A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power
+ 0.5 D
– 0.5 D
+ 0.2 D
– 0.2 D
A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his text book. Which of the following statements is correct?
The near point of his eyes has receded away
The near point of his eyes has come closer to him
The far point of his eyes has come closer to him
The far point of his eyes has receded away
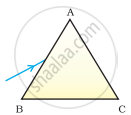
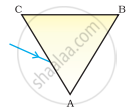
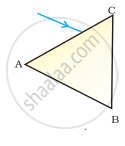
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in Figure . In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
 |
 |
 |
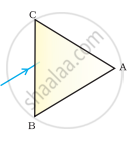 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
At noon the sun appears white as
light is least scattered
all the colours of the white light are scattered away
blue colour is scattered the most
red colour is scattered the most
The phenomena of light involved in the formation of rainbow are ______.
Reflection, refraction and dispersion
Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
dispersion of light by water droplets
refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
scattering of light by dust particles
internal reflection of light by clouds
The clear sky appears blue because
blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere
ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere
violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere
light of all other colours is scattered more than the violet and blue colour lights by the atmosphere
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in air?
Red light moves fastest
Blue light moves faster than green light
All the colours of the white light move with the same speed
Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light
The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in colour. These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colours, the red light
is scattered the most by smoke or fog
is scattered the least by smoke or fog
is absorbed the most by smoke or fog
Which of the following phenomena contributes significantly to the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
Dispersion of light
Scattering of light
Total internal reflection of light
Reflection of light from the earth
The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to
the presence of algae and other plants found in water
reflection of sky in water
scattering of light
absorption of light by the sea
When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the
crystalline lens
outer surface of the cornea
iris
pupil
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
contract and lens becomes thicker
are relaxed and lens becomes thicker
contract and lens becomes thinner
Which of the following statement is correct?
A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly
A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly
A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 11 The Human Eye and the Colourful World Short Answer Questions [Pages 88 - 89]
Draw ray diagram showing myopic eye.
Draw ray diagram showing hypermetropic eye.
A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the blackboard. What advice will a doctor give to her? Draw ray diagram for the correction of this defect.
How are we able to see nearby and also the distant objects clearly?
A person needs a lens of power –4.5 D for correction of her vision.
- What kind of defect in vision is she suffering from?
- What is the focal length of the corrective lens?
- What is the nature of the corrective lens?
How will you use two identical prisms so that a narrow beam of white light incident on one prism emerges out of the second prism as white light? Draw the diagram.
Draw a ray diagram showing the dispersion through a prism when a narrow beam of white light is incident on one of its refracting surfaces. Also indicate the order of the colours of the spectrum obtained.
Is the position of a star as seen by us its true position? Justify your answer.
Why do we see a rainbow in the sky only after rainfall?
Why is the colour of the clear sky blue?
What is the difference in colours of the Sun observed during sunrise/sunset and noon? Give explanation for each.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 11 The Human Eye and the Colourful World Long Answer Questions [Page 89]
Explain the structure and functioning of Human eye. How are we able to see nearby as well as distant objects?
When do we consider a person to be myopic or hypermetropic? Explain using diagrams how the defects associated with myopic and hypermetropic eye can be corrected?
Explain the refraction of light through a triangular glass prism using a labelled ray diagram. Hence define the angle of deviation.
How can we explain the reddish appearance of sun at sunrise or sunset? Why does it not appear red at noon?
Explain the phenomenon of dispersion of white light through a glass prism, using suitable ray diagram.
How does refraction take place in the atmosphere? Why do stars twinkle but not the planets?
Solutions for 11: The Human Eye and the Colourful World
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 11 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE 11 (The Human Eye and the Colourful World) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 10 chapter 11 The Human Eye and the Colourful World are Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Care of the Eyes, Refraction of Light Through a Prism, Scattering of Light and Its Types, Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum, Atmospheric Refraction, Applications of Scattering of Light, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Prism, Application of Atmospheric Refraction.
Using NCERT Exemplar Science [English] Class 10 solutions The Human Eye and the Colourful World exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 10 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, The Human Eye and the Colourful World Science [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
