Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Acids, Bases and Salts
3: Metals and Non-metals
4: Carbon and its Compounds
5: Periodic Classification of Elements
6: Life Processes
7: Control and Coordination
8: How do Organisms Reproduce?
9: Heredity and Evolution
10: Light – Reflection and Refraction
11: The Human Eye and the Colourful World
12: Electricity
▶ 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
14: Sources of Energy
15: Our Environment
16: Management of Natural Resources
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 13 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Science [English] Class 10.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Multiple Choice Questions [Pages 97 - 99]
Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of field
The direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points
Magnetic field lines are closed curves
If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength
Relative strength of magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines
If the key in the arrangement is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are
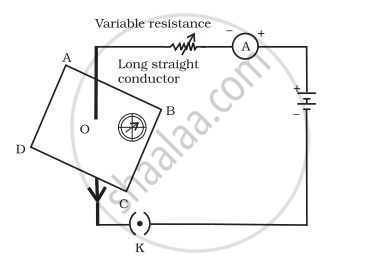
concentric circles
elliptical in shape
straight lines parallel to each other
concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it
A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of paper carries a current when the key is ON. The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anti clockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the face close to

A
B
A if the current is small, and B if the current is large
B if the current is small and A if the current is large
For a current in a long straight solenoid N- and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid
The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid
The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet
The N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed
A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper pointing from left to right as shown in Figure. In the field an electron and a proton move as shown. The electron and the proton experience

forces both pointing into the plane of paper
forces both pointing out of the plane of paper
forces pointing into the plane of paper and out of the plane of paper, respectively
force pointing opposite and along the direction of the uniform magnetic field respectively
Commercial electric motors do not use
an electromagnet to rotate the armature
effectively large number of turns of conducting wire in the current carrying coil
a permanent magnet to rotate the armature
a soft iron core on which the coil is wound
In the arrangement shown in Figure there are two coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod. Initially the key is not inserted. Then the key is inserted and later removed. Then
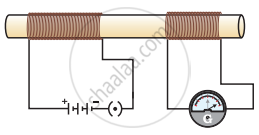
the deflection in the galvanometer remains zero throughout
there is a momentary deflection in the galvanometer but it dies out shortly and there is no effect when the key is removed
there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in the same direction
there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in opposite directions
Choose the incorrect statement
Fleming’s right-hand rule is a simple rule to know the direction of induced current
The right-hand thumb rule is used to find the direction of magnetic fields due to current carrying conductors
The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the direct current always flows in one direction, whereas the alternating current reverses its direction periodically
In India, the AC changes direction after every `1/50` second
A constant current flows in a horizontal wire in the plane of the paper from east to west as shown in Figure. The direction of magnetic field at a point will be North to South
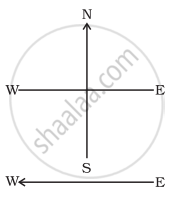
directly above the wire
directly below the wire
at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the north side of the wire
at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the south side of the wire
The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is
more at the ends than at the centre
minimum in the middle
same at all points
found to increase from one end to the other
To convert an AC generator into DC generator
split-ring type commutator must be used
slip rings and brushes must be used
a stronger magnetic field has to be used
a rectangular wire loop has to be used
The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short circuiting or overloading is
earthing
use of fuse
use of stabilizers
use of electric meter
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Short Answer Questions [Pages 100 - 101]
A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane of paper near point A as shown in Figure. In which plane should a straight current carrying conductor be placed so that it passes through A and there is no change in the deflection of the compass? Under what condition is the deflection maximum and why?

Under what conditions permanent electromagnet is obtained if a current carrying solenoid is used? Support your answer with the help of a labelled circuit diagram.
AB is a current carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as shown in Figure. What are the directions of magnetic fields produced by it at points P and Q? Given r1 > r2, where will the strength of the magnetic field be larger?

A magnetic compass shows a deflection when placed near a current carrying wire. How will the deflection of the compass get affected if the current in the wire is increased? Support your answer with a reason.
It is established that an electric current through a metallic conductor produces a magnetic field around it. Is there a similar magnetic field produced around a thin beam of moving
- alpha particles,
- neutrons? Justify your answer.
What does the direction of thumb indicate in the right-hand thumb rule. In what way this rule is different from Fleming’s left-hand rule?
Meena draws magnetic field lines of field close to the axis of a current carrying circular loop. As she moves away from the centre of the circular loop she observes that the lines keep on diverging.
How will you explain her observation.
What does the divergence of magnetic field lines near the ends of a current carrying straight solenoid indicate?
Name four appliances where in an electric motor, a rotating device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, is used as an important component. In what respect motors are different from generators?
What is the role of the two conducting stationary brushes in a simple electric motor?
What is the difference between a direct current and an alternating current? How many times does AC used in India change direction in one second?
What is the role of fuse, used in series with any electrical appliance? Why should a fuse with defined rating not be replaced by one with a larger rating?
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Long Answer Questions [Page 101]
Why does a magnetic compass needle pointing North and South in the absence of a nearby magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a current carrying loop is brought near it. Describe some salient features of magnetic lines of field concept.
With the help of a labelled circuit diagram illustrate the pattern of field lines of the magnetic field around a current carrying straight long conducting wire. How is the right hand thumb rule useful to find direction of magnetic field associated with a current carrying conductor?
Explain with the help of a labelled diagram the distribution of magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop. Why is it that if a current carrying coil has n turns the field produced at any point is n times as large as that produced by a single turn?
Describe the activity that shows that a current-carrying conductor experiences a force perpendicular to its length and the external magnetic field. How does Fleming’s left-hand rule help us to find the direction of the force acting on the current carrying conductor?
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a simple electric motor and explain its working. In what way these simple electric motors are different from commercial motors?
Explain the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. Describe an experiment to show that a current is set up in a closed loop when an external magnetic field passing through the loop increases or decreases.
Describe the working of an AC generator with the help of a labelled circuit diagram. What changes must be made in the arrangement to convert it to a DC generator?
Draw an appropriate schematic diagram showing common domestic circuits and discuss the importance of fuse. Why is it that a burnt out fuse should be replaced by another fuse of identical rating?
Solutions for 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE 13 (Magnetic Effects of Electric Current) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current are Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Properties of magnetic lines of force, Right-hand Thumb Rule, Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil), Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid), Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor, Electric Motor, Electromagnetic Induction, Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator, Household Electrical Circuits, Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, Electric Generator, Direct Current Motor, Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor, Types of Current.
Using NCERT Exemplar Science [English] Class 10 solutions Magnetic Effects of Electric Current exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 10 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 13, Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Science [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
