Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How can you differentiate between addition and condensation polymerisation?
उत्तर १
In addition polymerization, the molecules of the same or different monomers simply add on to one another leading to the formation of a macromolecules without elimination of small molecules like H2O, NH3 etc. Addition polymerization generally occurs among molecules containing double and triple bonds. For example, formation of polythene from ethene and neoprene from chloroprene, etc. In condensation polymerisation, two or more bifunctional trifimctional molecules undergo a series of independent condensation reactions usually with the elimination of simple molecules like water, alcohol, ammonia, carbon dioxide and hydrogen chloride to form a macromolecule. For example, nylon-6,6 is a condensation polymer of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid formed by elimination of water molecules
उत्तर २
Addition polymerization is the process of repeated addition of monomers, possessing double or triple bonds to form polymers. For example, polythene is formed by addition polymerization of ethene.
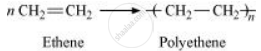
Condensation polymerization is the process of formation of polymers by repeated condensation reactions between two different bi-functional or tri-functional monomers. A small molecule such as water or hydrochloric acid is eliminated in each condensation. For example, nylon 6, 6 is formed by condensation polymerization of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following is a fibre? Nylon, neoprene, PVC
Write the names of monomer of the following polymer:

How is dacron obtained from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid?
How are the following polymers prepared?
Orlon
Write a note on aldol condensation.
What are thermoplastic polymers?
Name the monomers and the type of polymerization in each of the following polymers:
Bakelite
What is the significance of number of 6,6 in the polymer nylon-6,6?
Write the name of the monomer of the following polymer:
Nylon – 2 – Nylon – 6
Write the structures of monomers used the following polymers:
Nylon - 6, 6
Which of the following polymers can have strong intermolecular forces?
(i) Nylon
(ii) Polystyrene
(iii) Rubber
(iv) Polyesters
Which factor imparts crystalline nature to a polymer like nylon?
Assertion: Polyamides are best used as fibres because of high tensile strength.
Reason: Strong intermolecular forces (like hydrogen bonding within polyamides) lead to close packing of chains and increase the crystalline character, hence, provide high tensile strength to polymers
Acetic acid is added in the preparation of nylon-6 to
Nylon – 6 is made from
The polymer containing strong intermolecular forces, e.g., hydrogen bonding, is ______.
