Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery?
उत्तर
The energy given to each coulomb of charge equals the amount of work done to move it.
Now we know that,
Potential difference = `("Work Done")/("Charge")`
∴ Work done = Potential difference × charge
Where, Charge = 1 C and Potential difference = 6 V
∴ Work done = 6 × 1
= 6 Joule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the quantity of heat produced in a 20 Ω resistor carrying 2.5 A current in 5 minutes.
What is meant by saying that the electric potential at a point is 1 volt?
If a potential difference of 10 V causes a current of 2 A to flow for 1 minute, how much energy is transferred?
Name the law which relates the current in a conductor to the potential difference across its ends.
Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is halved. By how much does the current change?
Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. By how much does the current change?
A p.d. of 10 V is needed to make a current of 0.02 A flow through a wire. Wire p.d. is needed to make a current of 250 mA flow through the same wire?
Calculate the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
Explain the statement ‘the potential difference between two points is 1 volt’.
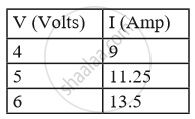
The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts.
What will be the nature of the graph between the current and potential difference? (Do not draw a graph.)
A current of 0.2 A flows through a wire whose ends are at a potential difference of 15 V. Calculate:
(i) The resistance of the wire, and
(ii) The heat energy produced in 1 minute.
What would you suggest to a student if while performing an experiment he finds that the pointer/needle of the ammeter and voltmeter do not coincide with the zero marks on the scales when the circuit is open? No extra ammeter/voltmeter is available in the laboratory.
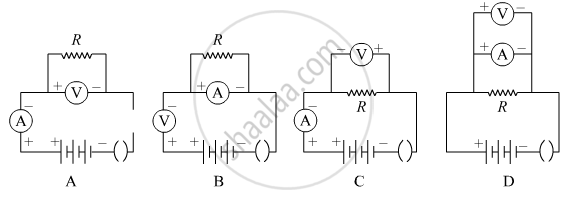
Which one of the following is the correct set-up for studying the dependence of the current on the potential difference across a resistor and why?
Point out two differences between e.m.f. and potential difference as applied to electric circuits.
A current of 0.2 A flows through a conducting wire for 5 minutes. How much charge will flow?
State Ohm’s law.
Twenty-seven drops of the same size are charged at 220 V each. They combine to form a bigger drop. Calculate the potential of the bigger drop.
Twenty-seven drops of same size are charged at 220 V each. They combine to form a bigger drop. Calculate the potential of the bigger drop.
Find the potential difference required to flow a current of 300 mA in a wire of resistance 20 Ω.
