Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How much heat energy is released when 5 g of water at 20° C changes to ice at 0° C?
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 ° C-1 Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1]
उत्तर
θ = mc Δ θ + mL
= 5 × 4.2 × 20 + 5 × 336
= 420 + 1680
= 2100 joule
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 x 10-2 kg of nitrogen (at room temperature) to raise its temperature by 45 °C at constant pressure? (Molecular mass of N2 = 28; R = 8.3 J mol-1 K-1.)
What property of water makes it an effective coolant?
A substance is in the form of a solid at 0°C. The amount of heat added to this substance and the temperature of the substance are plotted on the following graph:

If the specific heat capacity of the solid substance is 500 J/kg °G, find from the graph, the mass of the substance.
Calculate the amount of heat released when 5.0 g of water at 20°C is changed into ice at 0°C.
(Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g°C
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J/g)
Answer the following question.
Why do we generally consider two specific heats of a gas?
The specific heat capacity of water is 1 cal/g °C.
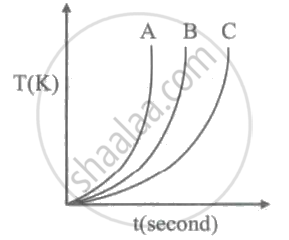
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific beat?
Match the following
| 1. | Specific heat capacity | a. | Dewar bottle |
| 2. | Calorimeter | b. | Lavoisier and Simon |
| 3. | Vacuum flask | c. | J Kg-1 K-1 |
| 4. | Ice – calorimeter | d. | Heat capacity |
When two kilocalories of heat are supplied to a system, the internal energy of the system increases by 5030 J and the work done by the gas against the external pressure is 3350 J. Calculate J, the mechanical equivalent of heat.
