Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
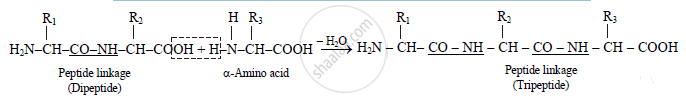
How is tripeptide formed?
उत्तर
b. The reaction of the COOH group of one amino acid molecule and NH2 group of the neighbouring amino acid molecule forms peptide having -CO-NH- linkage by
elimination of water

The dipeptide formed reacts with another molecule of amino acid to form tripeptide
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are proteins classified on the basis of molecular shapes?
Discuss the optical activity of lactic acid.
Define the following as related to proteins
Peptide linkage
Differentiate between the following :
Fibrous proteins and Globular proteins
Write one difference between α-helix and β-pleated structures of proteins.
Which of the following biomolecules is insoluble in water?
The helical structure of protein is stabilized by:
Which of the following statement is correct:
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by:
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like, change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Explain formation of peptide linkage in protein with an example.
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet structure.
Reason (R): The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Presence of disulphide link gives rise to which structure of protein?
Out of the following, which type of interaction is responsible for the stabilisation of the α-helix structure of proteins?
The correct structure of Ruhemann's Purple, the compound formed in the reaction of ninhydrin with proteins is:
An α-helix is a structural feature of ______.
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
