Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of the non-transition metals? Illustrate with examples.
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of the p-block elements?
उत्तर १
In transition elements, the oxidation state can vary from +1 to the highest oxidation state by removing all its valence electrons. Also, in transition elements, the oxidation states differ by 1 (Fe2+ and Fe3+; Cu+ and Cu2+). In non-transition elements, the oxidation states differ by 2, for example, +2 and +4 or +3 and +5, etc.
उत्तर २
The variability of oxidation states, a characteristic of transition elements, arises due to incomplete filling of d-orbitals in such a way that their oxidation states differ from each other by unity, e.g., Fe2+, Fe3+, Cr2+, Cr3+. This is in contrast with the variability of oxidation states of non-transition elements where oxidation states normally differ by a unit of two. i.e., Sn2+, Sn4+, P3+ and P5+, etc. in the p-block the lower oxidation states are favoured by the heavier members (due to inert pair effect), the opposite is true in the groups of J-block.For example, in group 6, Mo (VI) and W (VI) are found to be more stable than Cr (VI). Thus Cr (VI) in the form of dichromate in acidic medium is a strong oxidising agent, whereas MOO3 and WO3 are not.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are the transition elements? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
Account for the following:
Cu+ ion is unstable in aqueous solution.
Why is the highest oxidation state of a metal exhibited in its oxide or fluoride only?
What are the characteristics of the transition elements and why are they called transition elements?
Write balanced chemical equations for the conversion of `CrO_4^(2-)` to `Cr_2O_7^(2-)` in acidic medium and `Cr_2O_7^(2-)` to `CrO_4^(2-)`
in basic medium.
Why do transition metal ions possess a great tendency to form complexes?
Which of the following ions show higher spin only magnetic moment value?
(i) \[\ce{Ti^3+}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Mn2+}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Fe2+}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Co3+}\]
Why does copper not replace hydrogen from acids?
Ionisation enthalpies of Ce, Pr and Nd are higher than Th, Pa and U. Why?
Assertion: \[\ce{Cu^2+}\] iodide is not known.
Reason: \[\ce{Cu^2+}\] oxidises \[\ce{I^-}\] to iodine.
Why are fluorides of transition metals more stable in their higher oxidation state as compared to the lower oxidation state?
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
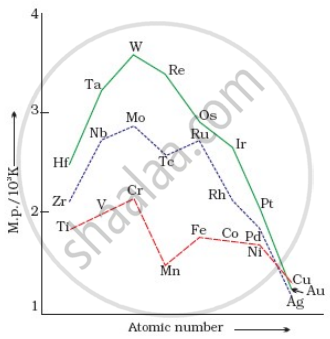
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
The element with atomic number 53 belongs to
The element with atomic number 46 belongs to
The basic character of transition metals monoxide follow the order.
Which of the following ions will exhibit colour in aqueous solution?
The oxidation state of Fe in [Fe(CO)5] is ______.
Which of the following characteristics of transition metals is associated with their catalytic activity?
Give two similarities in the properties of Sc and Zn.
The compounds of \[\ce{Ti^4+}\] ions are colourless due to ______.
