Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If 4 g of \[\ce{NaOH}\] dissolves in 36 g of \[\ce{H2O}\], calculate the mole fraction of each component in the solution. Also, determine the molarity of solution (specific gravity of solution is 1g mL–1).
उत्तर
Molar mass of \[\ce{NaOH}\] = 40 g/mole
Molar mass of water = 18 g/ mole
Mass of \[\ce{NaOH}\] = 4 g
Number of moles of NaOH = `(4 g)/(40 g)` = 0.1 mol
Number of moles of H2O = `(36 g)/(18 g)` = 2 mol
Mole fraction of water = `(26 g)/("Number of moles of NaOH" + "Number of moles of" H_2O)`
Mole fraction of NaOH = `2/(0.1 + 2) = 2/2.1` = 0.95
Number of moles of `2/0.1 = 0.1/2.1` = 0.047
Number of moles of \[\ce{NaOH}\]
Mass of solution = Mass of solute + Mass of solvent
Mass of \[\ce{NaOH}\] + Mass of water = 4 g + 36 g = 40 g
Specific gravity of solution = 1 g/ml
1 litre = 1000 ml volume of solution = 40 ml
∴ 40 ml = 0.04 litre
Molarity = `"Number of moles of solute"/"Volume in litre" = (0.1 "mol")/(0.04 "litre")` = 2.5 M
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the amount of carbon dioxide that could be produced when 1 mole of carbon is burnt in air.
Calculate the amount of carbon dioxide that could be produced when 2 moles of carbon are burnt in 16 g of dioxygen.
Explain the term mole fraction
Solve the following problem:
Find out the molar mass of the following compounds:
Copper sulphate crystal (CuSO4.5H2O)
(At. mass: Cu = 63.5; S = 32; O = 16; H = 1; Na = 23; C = 12; Fe = 56; N = 14)
Solve the following problem:
Find out the molar mass of the following compounds:
Mohr’s salt [FeSO4(NH4)2SO4.6H2O]
(At. mass: Cu = 63.5; S = 32; O = 16; H = 1; Na = 23; C = 12; Fe = 56; N = 14)
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
0.011 × 10−3
Solve the following problem:
Perform the following calculation. Round off your answer to three digits.
`(8.94xx10^6)/(4.35xx10^4)`
Solve the following problem:
Your laboratory partner was given the task of measuring the length of a box (approx 5 in) as accurately as possible, using a metre stick graduated in milimeters. He supplied you with the following measurements:
12.65 cm, 12.6 cm, 12.65 cm, 12.655 cm, 126.55 mm, 12 cm.
State which of the measurements you would accept, giving the reason.
Non-metals are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are non-lustrous, non-sonorous, non-malleable and are coloured.
Name a lustrous non-metal.
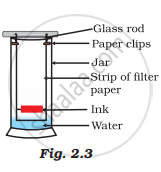
A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in Fig.2.3. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.
(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components?
(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
(iii) Suggest one more application of this technique.