Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
0.011 × 10−3
उत्तर
0.011 × 10−3 = 0.000011
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Explain the term Saturated solution giving examples.
Calculate the amount of carbon dioxide that could be produced when 1 mole of carbon is burnt in 16 g of dioxygen.
What is the concentration of sugar (C12H22O11) in mol L–1 if its 20 g are dissolved in enough water to make a final volume up to 2 L?
A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform, CHCl3, supposed to be carcinogenic in nature. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass).
- Express this in percent by mass.
- Determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
Calculate the molarity of a solution of ethanol in water in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.040 (assume the density of water to be one).
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
3.49 × 10−11
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
0.00477 × 105
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
5.00858585
Solve the following problem:
Perform the following calculation. Round off your answer to three digits.
`((9.28xx10^9)(9.9xx10^-7))/((511)(2.98xx10^-6))`
Solve the following problem:
A 1.000 mL sample of acetone, a common solvent used as a paint remover, was placed in a small bottle whose mass was known to be 38.0015 g.
The following values were obtained when the acetone - filled bottle was weighed: 38.7798 g, 38.7795 g and 38.7801 g. How would you characterise the precision and accuracy of these measurements if the actual mass of the acetone was 0.7791 g?
Name the process associated with the following
A drop of ink placed on the surface of water contained in a glass spreads throughout the water.
Non-metals are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are non-lustrous, non-sonorous, non-malleable and are coloured.
Name a lustrous non-metal.
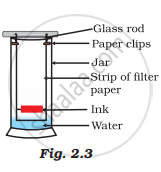
A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in Fig.2.3. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.
(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components?
(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
(iii) Suggest one more application of this technique.
What will be the molarity of a solution, which contains 5.85 g of NaCl(s) per 500 mL?
If the concentration of glucose \[\ce{(C6H12O6)}\] in blood is 0.9 g L–1, what will be the molarity of glucose in blood?
Sulphuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide as follows:
\[\ce{H2SO4 + 2NaOH -> Na2SO4 + 2H2O}\]
When 1 L of 0.1 M sulphuric acid solution is allowed to react with 1 L of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution, the amount of sodium sulphate formed and its molarity in the solution obtained is:
(i) 0.1 mol L–1
(ii) 7.10 g
(iii) 0.025 mol L–1
(iv) 3.55 g
Which of the following terms are unitless?
(i) Molality
(ii) Molarity
(iii) Mole fraction
(iv) Mass percent
If 4 g of \[\ce{NaOH}\] dissolves in 36 g of \[\ce{H2O}\], calculate the mole fraction of each component in the solution. Also, determine the molarity of solution (specific gravity of solution is 1g mL–1).
Match the following physical quantities with units
| Physical quantity | Unit |
| (i) Molarity | (a) g mL–1 |
| (ii) Mole fraction | (b) mol |
| (iii) Mole | (c) Pascal |
| (iv) Molality | (d) Unitless |
| (v) Pressure | (e) mol L–1 |
| (vi) Luminous intensity | (f) Candela |
| (vii) Density | (g) mol kg–1 |
| (viii) Mass | (h) Nm–1 |
| (i) kg |
An aqueous KCl solution of density 1.20 g mL-1 has a molality of 3.30 mol kg-1. The molarity of the solution in mol L-1 is ______. (Nearest integer)
250 g solution of D-glucose in water contains 10.8% of carbon by weight. The molality of the solution is nearest to ______.
(Given: Atomic weights are H, 1u; C, 12u; O, 16u)
The molality of solution containing 15.20 g of urea, (molar mass = 60) dissolved in 150 g or water is ______.
Molarity of liquid HCl will be if the density of the solution is 1.17 g/cc.
Find the molality of solution if boiling point increases by 1.75 K and molal elevation constant of solvent is 5K kg mol-1.
