Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, which of the following quantities remain conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact).
- Kinetic energy.
- Total linear momentum?
Give reason for your answer in each case.
उत्तर
The total linear momentum of the system of two balls is always conserved. While balls are in contact. there may be deformation which means elastic PE which came from the part of KE Therefore, KE may not be conserved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e. when they are in contact)?
A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with speed 200 m s–1 and angle 30° with the normal, and rebounds with the same speed. Is momentum conserved in the collision? Is the collision elastic or inelastic?
Which of the following potential energy curves in Fig. cannot possibly describe the elastic collision of two billiard balls? Here r is distance between centres of the balls.

Define coefficient of restitution.
Answer the following question.
Discuss the following as special cases of elastic collisions and obtain their exact or approximate final velocities in terms of their initial velocities.
- Colliding bodies are identical.
- A very heavy object collides on a lighter object, initially at rest.
- A very light object collides on a comparatively much massive object, initially at rest.
A bomb of mass 9 kg explodes into two pieces of mass 3 kg and 6 kg. The velocity of mass 3 kg is 16 m/s, The kinetic energy of mass 6 kg is ____________.
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in figure.
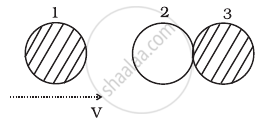
If the collision is elastic, which of the following (Figure) is a possible result after collision?
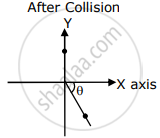
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity of 10`sqrt3` ms–1 along the X-axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y-axis at a speed of 10 m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle θ (degree) with respect to the X-axis.
The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure.
The value of θ to the nearest integer is ______.
A bag of sand of mass 9.8 kg is suspended by a rope. A bullet of 200 g travelling with speed 10 ms-1 gets embedded in it, then loss of kinetic energy will be ______.
The dimension of mutual inductance is ______.
