Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the circuit shown below, the voltmeter reads 10 V.
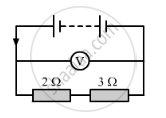
(a) What is the combined resistance?
(b) What current flows?
(c) What is the p.d. across 2 Ω resistor?
(d) What is the p.d. across 3 Ω resistor?
उत्तर
(a) The resistors of 2 Ω and 3 Ω are connected in series.
Therefore their combined resistance, R = R1 + R2
Here, R1=2 Ω
R2=3 Ω
So, the combined resistance, R = 2 Ω + 3 Ω
R = 5 Ω
(b) The current, I in the circuit can be calculated as:
V = IR
or I = 10 / 5 = 2 At)=R2R1+R2v(t)
(c) The p.d. across the 2 Ω resistor is:
V = IR
or V = `2xx2` = 4 V
(d) The p.d. across the 3 Ω resistor:
V = IR
or V = 2 x 3
or V = 6 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the unit of current.
What is the unit of electric current?
If the amount of electric charge passing through a conductor in 10 minutes is 300 C, the current flowing is:
(a) 30 A
(b) 0.3 A
(c) 0.5 A
(d) 5 A
What happens to the other bulbs in a series circuit if one bulb blows off?
State the S.I. units of electrical power.
Coulomb is the SI unit of ____________.
An ammeter is always placed in parallel with the circuit.
1020 electrons, each having a charge of 1.6 x 10-19 C, flows in a circuit V is 0.1s. What is the current in ampere?
