Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the circuit shown below, the voltmeter reads 10 V.
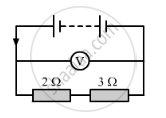
(a) What is the combined resistance?
(b) What current flows?
(c) What is the p.d. across 2 Ω resistor?
(d) What is the p.d. across 3 Ω resistor?
उत्तर
(a) The resistors of 2 Ω and 3 Ω are connected in series.
Therefore their combined resistance, R = R1 + R2
Here, R1=2 Ω
R2=3 Ω
So, the combined resistance, R = 2 Ω + 3 Ω
R = 5 Ω
(b) The current, I in the circuit can be calculated as:
V = IR
or I = 10 / 5 = 2 At)=R2R1+R2v(t)
(c) The p.d. across the 2 Ω resistor is:
V = IR
or V = `2xx2` = 4 V
(d) The p.d. across the 3 Ω resistor:
V = IR
or V = 2 x 3
or V = 6 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The SI unit of charge is volt.
An electric circuit consisting of a 0.5 m long nichrome wire XY, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and a plug key was set up.
(i) Draw a diagram of this electric circuit to study the relation between the potential difference maintained between the points 'X' and 'Y' and the electric current flowing through XY.
Draw a circuit diagram to show how two 4 V electric lamps can be lit brightly from two 2 V cells.
A given wire of resistance 1 Ω is stretched to double its length. What will be its new resistance?
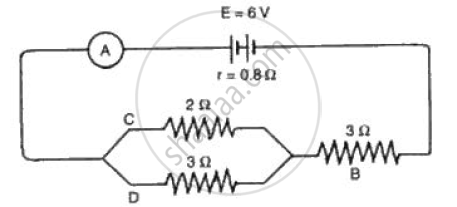
The circuit diagram (Fig.) shows a battery of e.m.f. 6 volts and internal
resistance of 0.8 Ω oonnected in series. Find the
(a) Current reoorded by the ammeter,
(b) P.d. across the terminals of the resistor B,
( c) Current passing through each of the resistors B, C and D, and
( d) P.d. across the terminals of the battery.
One unit of electrical energy consumed is equal to 1000 kilowatt-hour.
Which of the following represents voltage?
