Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the figure, structure of an antibody molecule is shown. Name the parts A, B and C. Show A, B and C in the diagram.

उत्तर
A - Constant region of heavy chain
B - Constant region of light chain
C - Variable region of light and heavy chain
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between Innate and acquired immunity.
______ results in the formation of AMIS.
The entire body is protected from attack from its own immune system due to the ______
Which type of resistance against pathogens does a human acquire through life?
Which type of immunity is provided by colostrum?
Which of the following is NOT a unique feature of acquired immunity?
Antibodies in our body are complex:
Transplantation of tissues/organs to save certain patients often fails due to rejection of such tissues/organs by the patient. Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections?
For an organ transplant, it is an advantage to have an identical twin. Why?
| When a microorganism invades a host, a definite sequence of events usually occurs leading to infection and disease, causing suffering to the host. This process is called pathogenesis. Once a microorganism overcomes the defence system of the host, development of the disease follows a certain sequence of events as shown in the graph. Study the graph given below for the sequence of events leading to the appearance of a disease and answer the questions that follow: |
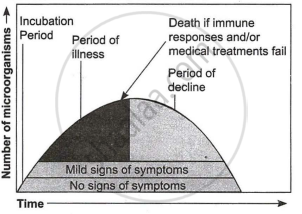
(a) In which period, according to the graph there are maximum chances of a person transmitting a disease/infection and why? (1)
(b) Study the graph and write what is an incubation period. Name a sexually transmitted disease that can be easily transmitted during this period. Name the specific type of lymphocytes that are attacked by the pathogen of this disease. (2)
OR
(b) Draw a schematic labelled diagram of an antibody. (2)
(c) In which period, the number of immune cells forming antibodies will be the highest in a person suffering from pneumonia? Name the immune cells that produce antibodies. (1)
