Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
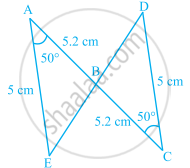
In the given figure, ΔBCD is isosceles with base BD and ∠BAE ≡∠DEA. Prove that AB ≡ ED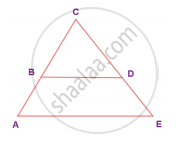
उत्तर
| Statements | Reasons |
| 1. ∠BAE ≡ ∠DEA | Given |
| 2. AC = EC | By (1) sides opposite to equal angles are equal |
| 3. BC = DC | Given BCD is isosceles with base BD |
| 4. AC – BC = EC – DC | 2 – 3 |
| 5. AB ≡ ED | By 4 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
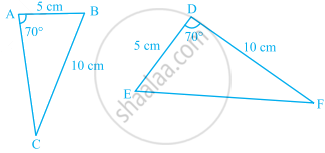
Given below are measurements of some parts of two triangles. Examine whether the two triangles are congruent or not, by using the SAS congruence rule. If the triangles are congruent, write them in symbolic form.
∆ABC, AB = 7 cm, BC = 5 cm, ∠B = 50°.
∆DEF, DE = 5 cm, EF = 7 cm, ∠E = 50°.
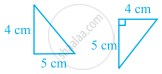
State whether the two triangles are congruent or not. Justify your answer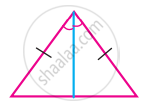
Construct a triangle XYZ with the given conditions.
BC = 8 cm, AC = 6 cm and ∠C = 40°
Construct a triangle PQR with given conditions.
∠P = 60°, ∠R = 35° and PR = 7.8 cm
In the given figures, two triangles are congruent by RHS.
In the given figure, which pairs of triangles are congruent by SAS congruence criterion (condition)? if congruent, write the congruence of the two triangles in symbolic form.
In the given figure, which pairs of triangles are congruent by SAS congruence criterion (condition)? if congruent, write the congruence of the two triangles in symbolic form.

In the given figure, which pairs of triangles are congruent by SAS congruence criterion (condition)? if congruent, write the congruence of the two triangles in symbolic form.
State which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent. If yes, write them in symbolic form (you may draw a rough figure).
∆PQR: PQ = 3.5 cm, QR = 4.0 cm, ∠Q = 60°
∆STU: ST = 3.5 cm, TU = 4 cm, ∠T = 60°
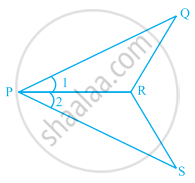
In the given figure, PO = PS and ∠1 = ∠2.
- Is ∆PQR ≅ ∆PSR? Give reasons.
- Is QR = SR? Give reasons.