Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
List any two contrasting characters other than height that Mendel used in his experiments in pea plants.
उत्तर
The two contrasting traits other than height used by Mendel are:-
(i) Pod colour - Green pod colour was dominant over yellow colour
(ii) Seed shape - Round seed shape was dominant over wrinkled seed shape
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do Mendel's experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
In a monohybrid cross between tall pea plants (TT) and short pea plants (tt), a scientist obtained only tall pea plants (Tt) in the F1 generation. However, on selfing the F1 generation pea plants, he obtained both tall and short plants in F2 generation. On the basis of above observations with other angiosperms also, can the scientist arrive at a law? If yes, explain the law. If not, give justification for your answer.
A cross between two individuals results in a ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 for four possible phenotypes of progeny. This is an example of a ______
In order to ensure that he had pure-breeding plants for his experiments, Mendel :
(a) cross-fertilised each variety with each other
(b) let each variety self fertilise for several generations
(c) removed the female parts of the plants
(d) removed the male parts of the plants.
A pregnant woman has an equal chance of her baby being blood group A or blood group AB. Which one of the following shows the possible genotypes of the woman and the father of her child?
(a) IA IA and IB IO
(b) IA IB and IB IO
(c) IA IO and IB IO
(d) IA IB and IA IO
A trait in an organism is influenced by ______
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) for every hormone there is a gene
(b) for every protein there is a gene
(c) for production of every enzyme there is a gene
(d) for every type of fat there is a gene
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O - is dominant? Why or why not?
Explain Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. Give one example.
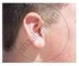
Figures (a) to (d) given below represent the type of ear lobes present in a family consisting of 2 children - Rahul, Nisha and their parents.
|
(a) Rahul's Father |
(b) Rahul |
(c) Rahul's Mother |
(d) Rahul's sister Nisha |
|
(e) |
(f) |
||
| Types of ear lobes | |||
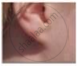
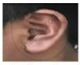
Excited by his observation of different types of ear lobes present in his family, Rahul conducted a survey of the type of ear lobes found {Figure (e) and (f)} in his classmates. He found two types of ear lobes in his classmates as per the frequency given below:
| Sex | Free | Attached |
| Male | 36 | 14 |
| Female | 31 | 19 |
On the basis of the above data answer the following questions.
- Which of the two characteristics - ‘free ear lobe’ or ‘attached ear lobe’ appears to be dominant in this case? Why?
- Is the inheritance of the free ear lobe linked with the sex of the individual? Give a reason for your answer.
- What type of ear lobe is present in father, mother, Rahul and his sister Nisha? Write the genetic constitution of each of these family members which explains the inheritance of this character in this family.
(Gene for the Free ear lobe is represented by F and the gene for the attached ear lobe is represented by f for writing the genetic constitution).
OR
Suresh’s parents have attached ear lobes. What type of ear lobe can be seen in Suresh and his sister Siya? Explain by giving the genetic composition of all.