Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Long answer question.
Explain the properties of an enzyme?
थोडक्यात उत्तर
उत्तर
- Proteinaceous Nature:
All enzymes are basically made up of protein. - Three-Dimensional conformation:
- All enzymes have specific 3-dimensional conformation.
- They have one or more active sites to which substrate (reactant) combines.
- The points of the active site where the substrate joins with the enzyme is called the substrate-binding site.
- Catalytic property:
- Enzymes are like inorganic catalysts and influence the speed of biochemical reactions but themselves remain unchanged.
- After completion of the reaction and release of the product, they remain active to catalyze again.
- A small number of enzymes can catalyze the transformation of a very large quantity of the substrate into an end product.
- For example, sucrase can hydrolyze 100000 times of sucrose as compared with its own weight.
- Specificity of action:
- The ability of an enzyme to catalyze one specific reaction and essentially no other is perhaps its most significant property. Each enzyme acts upon a specific substrate or a specific group of substrates.
- Enzymes are very sensitive to temperature and pH.
- Each enzyme exhibits its highest activity at a specific pH i.e. optimum pH.
- Any increase or decrease in pH causes a decline in enzyme activity e.g. enzyme pepsin (secreted in stomach) shows the highest activity at an optimum pH of 2 (acidic).
- Trypsin (in the duodenum) is most active at an optimum pH of 9.5 (alkaline).
- Both these enzymes viz. pepsin and trypsin are protein-digesting enzymes.
- Temperature:
- Enzymes are destroyed at a higher temperature of 60-70°C or below, they are not destroyed but become inactive.
- This inactive state is temporary and the enzyme can become active at a suitable temperature.
- Most of the enzymes work at an optimum temperature between 20°C and 35°C.
shaalaa.com
Biomolecules in the Cell
या प्रश्नात किंवा उत्तरात काही त्रुटी आहे का?
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the peptide bond.
Answer the following question.
Explain the secondary structure of a protein with examples.
Answer the following question.
Explain the induced fit model for the mode of enzyme action.
Answer the following question.
What is RNA? Enlist types of RNA.
Complete the following chart.
| Protein | Physiological role |
| Collagen | ___________ |
| __________ | Responsible for muscle contraction |
| Immunoglobulin IgG | ___________ |
| ___________ | Significant in respiration |
| Fibrinogen | ____________ |
Answer the following with reference to the following figure.
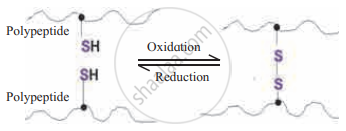
- Name the type of bond formed between two polypeptides.
- Which amino acid is involved in the formation of such bond?
- Amongst I, II, III and IV structural level of protein, which level of structure includes such bond?
Long answer question.
Describe the factors affecting enzyme action.
Long answer question.
Enlist the point of differences among DNA and RNA.
Name the form in which carbohydrate is transported in a plant.
Name the reagent used for testing for reducing sugar.
