Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Long answer question.
How are enzymes classified? Mention an example of each class.
उत्तर
Enzymes are classified into six classes:
- Oxidoreductases: These enzymes catalyze oxidation and reduction reactions by the transfer of hydrogen and/or oxygen.
e.g. alcohol dehydrogenase
\[\ce{Alcohol + NAD^+ ->[Alcohol][dehydroenase] Aldehyde + NADH2}\] - Transferases: These enzymes catalyse the transfer of certain groups between two molecules. e.g. glucokinase
\[\ce{Glucose + ATP ->[Glucokinase] Glucose – 6 – Phosphate + ADP}\] - Hydrolases: These enzymes catalyze hydrolytic reactions. This class includes amylases, proteases, lipases etc. e.g. Sucrase
\[\ce{Sucrose + water ->[Sucrase] Glucose + Fructose}\] - Lyases: These enzymes are involved in elimination reactions resulting in the removal of a group of atoms from the substrate molecule to leave a double bond. It includes aldolases, decarboxylases, and dehydratases, e.g. fumarate hydratase.
\[\ce{Histidine ->[Histidine][deca rbox ylase]Histamine + CO2}\] - Isomerases: These enzymes catalyze structural rearrangements within a molecule. Their nomenclature is based on the type of isomerism. Thus, these enzymes are identified as racemases, epimerases, isomerases, mutases, e.g. xylose isomerase.
\[\ce{Glucose – 6 – Phosphate ->[Isomerase] Fructose – 6 – Phosphate}\] - Ligases or Synthetases: These are the enzymes which catalyze the covalent linkage of the molecules utilizing the energy obtained from hydrolysis of an energy-rich compound like ATP, GTP e.g. glutathione synthetase, Pyruvate carboxylase.
\[\ce{Pyruvate + CO2 + ATP ->[Pyruvate][ca rbox ylase] Oxaloacetate + ADP + Pi}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Observe the following figure and name the type of bond shown by the arrow in the structure.

Answer the following question.
Enlist the examples of simple protein and add their significance.
Answer the following question.
Explain the secondary structure of a protein with examples.
Answer the following question.
Explain the induced fit model for the mode of enzyme action.
Answer the following question.
Describe the concept of metabolic pool.
Answer the following with reference to the following figure.
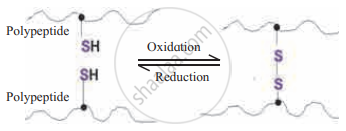
- Name the type of bond formed between two polypeptides.
- Which amino acid is involved in the formation of such bond?
- Amongst I, II, III and IV structural level of protein, which level of structure includes such bond?
Long answer question.
What are the nucleic acids?
Long answer question.
How metabolic pool is formed in the cell.
Insulin is a/an
The most abundant molecule in cell is ______.
