Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a virtual image by a converging mirror.
Mark clearly the pole, focus, centre of curvature and position of object in each case.
उत्तर
A virtual image is formed by a converging lens when an object is placed between the pole and the focus:
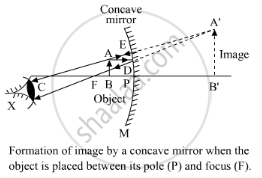
Here, P: pole, F: focus, C: centre of curvature, AB: object and A'B': image
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ......... to the mirror.
Give two uses of concave mirrors. Explain why you would choose concave mirrors for these uses.
Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is places in front of a concave mirror (converging mirror):
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between its centre of curvature and focus
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
A real image of an object is to be obtained. The mirror required for this purpose is:
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) either convex or concave
A student has focused the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a concave mirror. The situation is as given below:
Length of the flame = 1.5 cm
Distance of flame from the mirror = 18 cm
If the flame is perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror, then calculate the following:
- Distance of the image from the mirror
- Length of the image
If the distance between the mirror and the flame is reduced to 10 cm, then what would be observed on the screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer for this situation.
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
______ mirrors magnify the object placed close to them.
What is a concave and convex mirror?
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distance with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object-distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Given reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length) which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
