Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the defects given in Column I with the statements in given Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Simple vacancy defect | (a) shown by non-ionic solids and increases density of the solid. |
| (ii) Simple interstitial defect | (b) shown by ionic solids and decreases density of the solid. |
| (iii) Frenkel defect | (c) shown by non ionic solids and density of the solid decreases. |
| (iv) Schottky defect | (d) shown by ionic solids and density of the solid remains the same. |
उत्तर
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Simple vacancy defect | (c) shown by non ionic solids and density of the solid decreases. |
| (ii) Simple interstitial defect | (a) shown by non-ionic solids and increases density of the solid. |
| (iii) Frenkel defect | (d) shown by ionic solids and density of the solid remains the same. |
| (iv) Schottky defect | (b) shown by ionic solids and decreases density of the solid. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The following diagram shows:
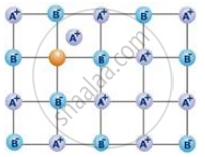
Which is not correct about the Schottky defects?
Assertion: No compound has both Schottky and Frenkel defects.
Reason: Both defects change the density of the solid.
Alkali halids do not show Frenkel defect because ____________.
In a Schottky defect ____________.
Cations are present in the interstitial sites in ______.
Schottky defect is observed in crystals when ______.
Which of the following point defects are shown by AgBr(s) crystals?
- Schottky defect
- Frenkel defect
- Metal excess defect
- Metal deficiency defect
Which of the following defects decrease the density?
(i) Interstitial defect
(ii) Vacancy defect
(iii) Frankel defect
(iv) Schottky defect
If NaCl is doped with 10–4 mole percent of SrCl2 the concentration of cation vacancies will be
