Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Monochromatic light of wavelength 600 nm is incident from the air on a water surface. The refractive index of water is 1.33. Find the
- wavelength,
- frequency and
- speed, of reflected and refracted light.
उत्तर
Given: λ = 600 nm, µ = 1.33
(i) In reflection, the ray will reflect back in the same medium as that of the incident ray.
Hence, wavelength (λ) = 600 nm
(ii) Frequency = υ = `"c"/λ = (3 xx 10^8)/(600 xx 10^-9)`
= 0.5 × 1015 Hz
(iii) Speed = 3 × 108 ms−1
In refraction, the speed and wavelength change while the frequency remains the same.
Hence, speed = ν = `"c"/µ = (3 xx 10^8)/(1.33)`
= 2.26 × 108 ms−1
Wavelength = λ = `ν/υ`
= `(2.26 xx 10^8)/(0.5 xx 10^15)`
= 4.52 × 10−7 m
= 452 nm
Frequency = υ = 0.5 × 1015 Hz
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
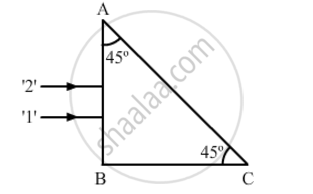
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.3 and 1.5. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
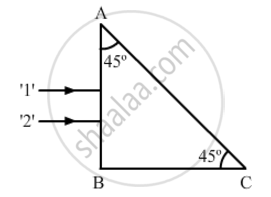
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.35 and 1.45. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
In the wave picture of light, the intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of light?
What kind of fringes do you expect to observe if white light is used instead of monochromatic light?
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The two slits S1 and S2 placed symmetrically around the central line are illuminated by a monochromatic light of wavelength λ. The separation between the slits is d. The light transmitted by the slits falls on a screen ∑1placed at a distance D from the slits. The slit S3 is at the central line and the slit S4 is at a distance z from S3. Another screen ∑2 is placed a further distance D away from ∑1.Find the ratio of the maximum to minimum intensity observed on ∑2 if z is equal to
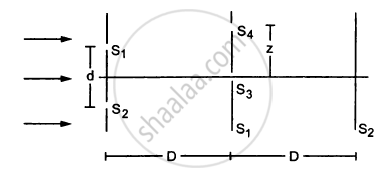
(a) \[z = \frac{\lambda D}{2d}\]
(b) \[\frac{\lambda D}{d}\]
(c) \[\frac{\lambda D}{4d}\]
Monochromatic fight of wavelength 198 nm is incident on the surface of a metallic cathode whose work function is 2.5 eV How much potential difference must be applied between the cathode and the anode of a photocell to just stop the photocurrent from flowing?
Answer the following question.
In the diffraction due to a single slit experiment, the aperture of the slit is 3 mm. If monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm is incident normally on the slit, calculate the separation between the first order minima and the 3rd order maxima on one side of the screen. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.5 m.
For constructive interference to take place between two monochromatic light waves of wavelength λ, the path difference should be ______.
The Figure below shows a ray of monochromatic light LM incident on the first surface AB of a regular (equilateral) glass prism ABC. The emergent ray grazes the adjacent surface AC. Calculate the angle of incidence. (Refractive Index of glass = 1.5)

