Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Monochromatic light of wavelength 600 nm is incident from the air on a water surface. The refractive index of water is 1.33. Find the
- wavelength,
- frequency and
- speed, of reflected and refracted light.
उत्तर
Given: λ = 600 nm, µ = 1.33
(i) In reflection, the ray will reflect back in the same medium as that of the incident ray.
Hence, wavelength (λ) = 600 nm
(ii) Frequency = υ = `"c"/λ = (3 xx 10^8)/(600 xx 10^-9)`
= 0.5 × 1015 Hz
(iii) Speed = 3 × 108 ms−1
In refraction, the speed and wavelength change while the frequency remains the same.
Hence, speed = ν = `"c"/µ = (3 xx 10^8)/(1.33)`
= 2.26 × 108 ms−1
Wavelength = λ = `ν/υ`
= `(2.26 xx 10^8)/(0.5 xx 10^15)`
= 4.52 × 10−7 m
= 452 nm
Frequency = υ = 0.5 × 1015 Hz
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency.
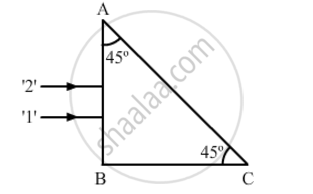
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.3 and 1.5. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
A monochromatic ray of light falls on a regular prism. What is the relation between the angle of incidence and angle of emergence in the case of minimum deviation?
When monochromatic light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, explain the following, giving reasons:
(i) Is the frequency of reflected and refracted light same as the frequency of incident light?
(ii) Does the decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by light wave?
Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
Monochromatic light of wavelength 650 nm falls normally on a slit of width 1.3 x 10-4 cm and the resulting Fraunhofer diffraction is obtained on a screen. Find the angular width of the . central maxima.
(a) Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
(b) The intensity at the central maximum (O) in Young's double-slit experimental set-up shown in the figure is IO. If the distance OP equals one-third of the fringe width of the pattern, show that the intensity at point P, would `"I"_°/4`
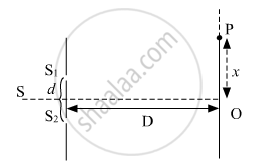
(c) In Young's double-slit experiment, the slits are separated by 0⋅5 mm and the screen is placed 1⋅0 m away from the slit. It is found that the 5th bright fringe is at a distance of 4⋅13 mm from the 2nd dark fringe. Find the wavelength of light used.
Using the monochromatic light of the wavelength in the experimental set-up of the diffraction pattern as well as in the interference pattern where the slit separation is 1 mm, 10 interference fringes are found to be within the central maximum of the diffraction pattern. Determine the width of the single slit, if the screen is kept at the same distance from the slit in the two cases.
A ray of monochromatic light propagating in the air is incident on the surface of the water. Which of the following will be the same for the reflected and refracted rays?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 396 nm is incident on the surface of a metal whose work function is 1.125 eV. Calculate:
- the energy of an incident photon in eV.
- the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons in eV.
