Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Nitrogen has positive electron gain enthalpy whereas oxygen has negative. However, oxygen has lower ionisation enthalpy than nitrogen. Explain.
उत्तर
The outermost electronic configuration of nitrogen is `2s^2 2p_x^1 2p_y^1 2p_z^1`. It is stable because it has exactly half-filled 2p-subshell. Therefore, it has no tendency to accept extra electron and energy has to be supplied to add additional electron. Thus, electron gain enthalpy of nitrogen is slightly positive. On the other hand, the outermost electronic configuration of O is `2s^2 2p_x^2 2p_y^1 2p_z^1`. It has higher positive charge (+8) than nitrogen (+7) and lower atomic size than N. Therefore, it has a tendency to accept an extra electron. Thus, electron gain enthalpy of O is negative. However, oxygen has four electrons in the 2p subshell and can lose one electron to acquire stable half-filled configuration and therefore, it has low ionization enthalpy. Because of stable configuration of N, it cannot readily lose electron and therefore, its ionization enthalpy is higher than that of O.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is –2.18 × 10–18 J. Calculate the ionization enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of J mol–1.
Hint: Apply the idea of mole concept to derive the answer.
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the
order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne.
Explain why O has lower ΔiH than N and F?
How would you explain the fact that the first ionization enthalpy of sodium is lower than that of magnesium but its second ionization enthalpy is higher than that of magnesium?
Explain the deviation in ionisation enthalpy of some elements from the general trend by using the given figure.
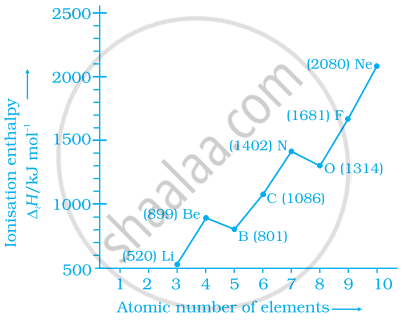
In general, the property (magnitudes only) that shows an opposite trend in comparison to other properties across a period is ______.
Consider the elements Mg, Al, S, P and Si, the correct increasing order of their first ionization enthalpy is ______.
For the gaseous reaction, \[\ce{K_{(g)} + F_{(g)} -> K^+_{ (g)} + F^-_{ (g)}}\], ΔH was calculated to be 19 kcal/mol under conditions where the cations and anions were prevented by electrostatic separation from combining with each other. The ionisation energy of K is 4.3 eV. The electron affinity of F is ______. (in eV)
`"A"_0/2` atoms of X(g) are converted into X+(g) by absorbing energy E1. `"A"_0/2` ions of X+(g) are converted into X−(g) with release of energy E2. Hence ionization energy and electron affinity of X(g) are ______.
The decreasing order of the second ionization potential of K, Ca and Ba is ______.
Which of the following atoms has the highest first ionization energy?
