Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
No work is done by a force on an object if
(a) the force is always perpendicular to its velocity
(b) the force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
(c) the object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object
(d) the object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
उत्तर
(a) the force is always perpendicular to its velocity
(c) the object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object
(d) the object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
No work is done by a force on an object if the force is always perpendicular to its velocity. Acceleration does not always provide the direction of motion, so we cannot say that no work is done by a force on an object if it is always perpendicular to the acceleration. Work done is zero when the displacement is zero.
In a circular motion, force provides the centripetal acceleration. The angle between this force and the displacement is 90° , so work done by the force on an object is zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A lawyer alleges in court that the police had forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this ?
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
Mark the correct statements :
(a) The nuclear force between two protons is always greater than the electromagnetic force between them.
(b) The electromagnetic force between two protons is always greater than the gravitational force between them.
(c) The gravitational force between two protons may be greater than the nuclear force between them.
(d) Electromagnetic force between two protons may be greater than the nuclear force acting between them.
Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
A satellite is projected vertically upwards from an earth station. At what height above the earth's surface will the force on the satellite due to the earth be reduced to half its value at the earth station? (Radius of the earth is 6400 km.)
Two charged particles placed at a separation of 20 cm exert 20 N of Coulomb force on each other. What will be the force of the separation is increased to 25 cm?
The work done by the external forces on a system equals the change in
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A block of mass 5.0 kg slides down an incline of inclination 30° and length 10 m. Find the work done by the force of gravity.
A force \[F = \alpha + bx\] acts on a particle in the x-direction, where a and b are constants. Find the work done by this force during a displacement from x = 0 to x = d.
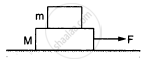
A block of mass m is kept over another block of mass M and the system rests on a horizontal surface (In the following figure). A constant horizontal force F acting on the lower block produces an acceleration \[\frac{F}{2 \left( m + M \right)}\] in the system, and the two blocks always move together. (a) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bigger block and the horizontal surface. (b) Find the frictional force acting on the smaller block. (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the smaller block by the bigger block during a displacement d of the system.
A box weighing 2000 N is to be slowly slid through 20 m on a straight track with friction coefficient 0⋅2 with the box. (a) Find the work done by the person pulling the box with a chain at an angle θ with the horizontal. (b) Find the work when the person has chosen a value of θ, which ensures him the minimum magnitude of the force.
A particle of mass m moves on a straight line with its velocity varying with the distance travelled, according to the equation \[\nu = a\sqrt{x}\] , where a is a constant. Find the total work done by all the forces during a displacement from \[x = 0 \text{ to } x - d\] .
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A block of mass 2.0 kg is pushed down an inclined plane of inclination 37° with a force of 20 N acting parallel to the incline. It is found that the block moves on the incline with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If the block started from rest, find the work done (a) by the applied force in the first second, (b) by the weight of the block in the first second and (c) by the frictional force acting on the block in the first second. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Force acting on a particle is (2`hat"i"` + 3 `hat"j"`) N. Work done by this force is zero, when a particle is moved on the line 3y + kx = 5. Here value of k is ______.
