Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The work done by the external forces on a system equals the change in
पर्याय
total energy
kinetic energy
potential energy
none of these
उत्तर
total energy
When work is done by an external forces on a system, the total energy of the system will change.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A boy is sitting on a chair placed on the floor of a room. Write as many action-reaction pairs of forces as you can.
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
List all the forces acting on (a) the pulley A, (b) the boy and (c) the block C in figure.
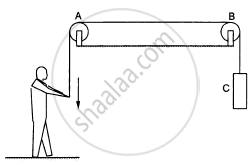
Figure shows a cart. Complete the table shown below.
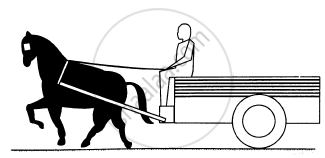
| Force on | Force by | Nature of the Force | Direction |
| Cart |
1 |
||
| Horse |
1 |
||
| Driver |
1 |
Let E, G and N represent the magnitudes of electromagnetic gravitational and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation. Then
Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
Two charged particles placed at a separation of 20 cm exert 20 N of Coulomb force on each other. What will be the force of the separation is increased to 25 cm?
The force with which the earth attracts an object is called the weight of the object. Calculate the weight of the moon from the following data : The universal constant of gravitation G = 6.67 × 11−11 N−m2/kg2, mass of the moon = 7.36 × 1022 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and the distance between the earth and the moon = 3.8 × 105 km.
Find the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force to the gravitational force acting between two protons.
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
Find the average force needed to accelerate a car weighing 500 kg from rest to 72 km/h through a distance of 25 m.
A particle of mass m moves on a straight line with its velocity varying with the distance travelled, according to the equation \[\nu = a\sqrt{x}\] , where a is a constant. Find the total work done by all the forces during a displacement from \[x = 0 \text{ to } x - d\] .
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Water falling from a 50-m high fall is to be used for generating electric energy. If \[1 \cdot 8 \times {10}^5 \text{ kg } \] of water falls per hour and half the gravitational potential energy can be converted into electrical energy, how many 100 W lamps can be lit with the generated energy?
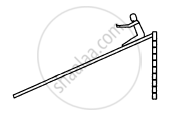
In a children's park, there is a slide which has a total length of 10 m and a height of 8⋅0 m . A vertical ladder is provided to reach the top. A boy weighing 200 N climbs up the ladder to the top of the slide and slides down to the ground. The average friction offered by the slide is three tenth of his weight. Find (a) the work done by the ladder on the boy as he goes up; (b) the work done by the slide on the boy as he comes down. Neglect any work done by forces inside the body of the boy
A uniform chain of mass m and length l overhangs a table with its two third part on the table. Find the work to be done by a person to put the hanging part back on the table.
A particle of mass m is kept on a fixed, smooth sphere of radius R at a position where the radius through the particle makes an angle of 30° with the vertical. The particle is released from this position. (a) What is the force exerted by the sphere on the particle just after the release? (b) Find the distance travelled by the particle before it loses contact with the sphere.
A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y-direction where F is in newton and y in metre. Work done by this force to move the particle from y – 0 to y – 1 m is:
