Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
उत्तर
Given:
\[\text{ Distance coverd by the man, s = 40 m } \]
\[\text{Acceleration of the man, a = 0 . 5 m} / s^2\]
\[\text{ F = ma } \]
\[ = 2 \times \left( 0 . 5 \right)\]
\[ = 1 N\]
\[\text{ Work done by the man on the block, } W = F \cdot S\]
\[ = 1 \times 40\]
\[ = 40 J\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A lawyer alleges in court that the police had forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this ?
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
A neutron exerts a force on a proton which is
(a) gravitational
(b) electromagnetic
(c) nuclear
(d) weak
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
The force with which the earth attracts an object is called the weight of the object. Calculate the weight of the moon from the following data : The universal constant of gravitation G = 6.67 × 11−11 N−m2/kg2, mass of the moon = 7.36 × 1022 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and the distance between the earth and the moon = 3.8 × 105 km.
Find the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force to the gravitational force acting between two protons.
The average separation between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state is 5.3 × 10−11 m. (a) Calculate the Coulomb force between them at this separation. (b) When the atom goes into its first excited state the average separation between the proton and the electron increases to four times its value in the ground state. What is the Coulomb force in this state?
The magnetic force on a charged particle is always perpendicular to its velocity. Can the magnetic force change the velocity of the particles? Speed of the particle?
A particle moves from a point \[\overrightarrow{r}_1 = \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] to another point
\[\overrightarrow{r}_2 = \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] acts on it. Find the work done by the force on the particle during the displacement.
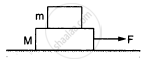
A block of mass m is kept over another block of mass M and the system rests on a horizontal surface (In the following figure). A constant horizontal force F acting on the lower block produces an acceleration \[\frac{F}{2 \left( m + M \right)}\] in the system, and the two blocks always move together. (a) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bigger block and the horizontal surface. (b) Find the frictional force acting on the smaller block. (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the smaller block by the bigger block during a displacement d of the system.
Find the average frictional force needed to stop a car weighing 500 kg at a distance of 25 m if the initial speed is 72 km/h.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the work done by the force of gravity in that one second if the work done by the applied force is 40 J.
A block of mass 2.0 kg is pushed down an inclined plane of inclination 37° with a force of 20 N acting parallel to the incline. It is found that the block moves on the incline with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If the block started from rest, find the work done (a) by the applied force in the first second, (b) by the weight of the block in the first second and (c) by the frictional force acting on the block in the first second. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A uniform chain of mass m and length l overhangs a table with its two third part on the table. Find the work to be done by a person to put the hanging part back on the table.
A particle of mass m is kept on a fixed, smooth sphere of radius R at a position where the radius through the particle makes an angle of 30° with the vertical. The particle is released from this position. (a) What is the force exerted by the sphere on the particle just after the release? (b) Find the distance travelled by the particle before it loses contact with the sphere.
A bicyclist comes to a skidding stop in 10 m. During this process, the force on the bicycle due to the road is 200 N and is directly opposed to the motion. The work done by the cycle on the road is ______.
A body is being raised to a height h from the surface of earth. What is the sign of work done by gravitational force?
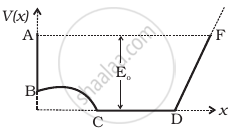
A graph of potential energy V(x) verses x is shown in figure. A particle of energy E0 is executing motion in it. Draw graph of velocity and kinetic energy versus x for one complete cycle AFA.
A block of mass m is taken from A to B slowly under the action of a constant force R Work done by this force is ______.

