Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The average separation between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state is 5.3 × 10−11 m. (a) Calculate the Coulomb force between them at this separation. (b) When the atom goes into its first excited state the average separation between the proton and the electron increases to four times its value in the ground state. What is the Coulomb force in this state?
उत्तर
Average separation between the proton and the electron of a Hydrogen atom in ground state, r = 5.3 × 10−11 m
(a) Coulomb force when the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state
\[F = 9 \times {10}^9 \times \frac{q_1 q_2}{r_2}\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times \left( 1 . 6 \times {10}^{- 19} \right)^2}{\left( 5 . 3 \times {10}^{- 11} \right)^2} = 8 . 2 \times {10}^{- 8} \text{N}\]
(b) Coulomb force when the average distance between the proton and the electron becomes 4 times that of its ground state
\[\text {Coulomb force, F } = \frac{1}{4\pi \in_0} = \frac{q_1 q_2}{\left( 4r \right)^2}\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times \left( 1 . 6 \times {10}^{- 19} \right)^2}{16 \times \left( 5 . 3 \right)^2 \times {10}^{- 22}}\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times \left( 1 . 6 \right)^2}{10 \times \left( 5 . 3 \right)^2} \times {10}^{- 7} \]
\[ = 0 . 0512 \times {10}^{- 7} \]
\[ = 5 . 1 \times {10}^{- 9} \text{ N }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
List all the forces acting on the block B in figure.
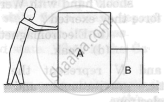
Figure shows a cart. Complete the table shown below.
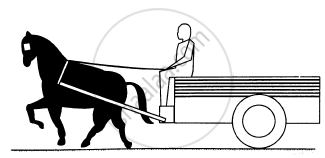
| Force on | Force by | Nature of the Force | Direction |
| Cart |
1 |
||
| Horse |
1 |
||
| Driver |
1 |
Let E, G and N represent the magnitudes of electromagnetic gravitational and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation. Then
A proton exerts a force on a proton which is
(a) gravitational
(b) electromagnetic
(c) nuclear
(d) weak
A monkey is sitting on a tree limb. The limb exerts a normal force of 48 N and a frictional force of 20 N. Find the magnitude of the total force exerted by the limb on the monkey.
The magnetic force on a charged particle is always perpendicular to its velocity. Can the magnetic force change the velocity of the particles? Speed of the particle?
The work done by the external forces on a system equals the change in
A small block of mass m is kept on a rough inclined surface of inclination θ fixed in an elevator. the elevator goes up with a uniform velocity v and the block does not slide on the wedge. The work done by the force of friction on the block in time t will be
A block of mass 5.0 kg slides down an incline of inclination 30° and length 10 m. Find the work done by the force of gravity.
A constant force of 2⋅5 N accelerates a stationary particle of mass 15 g through a displacement of 2⋅5 m. Find the work done and the average power delivered.
Find the average force needed to accelerate a car weighing 500 kg from rest to 72 km/h through a distance of 25 m.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Show that the work done by the applied force does not exceed 40 J.
A 250 g block slides on a rough horizontal table. Find the work done by the frictional force in bringing the block to rest if it is initially moving at a speed of 40 cm/s. If the friction coefficient between the table and the block is 0⋅1, how far does the block move before coming to rest?
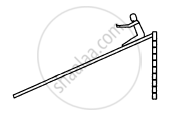
In a children's park, there is a slide which has a total length of 10 m and a height of 8⋅0 m . A vertical ladder is provided to reach the top. A boy weighing 200 N climbs up the ladder to the top of the slide and slides down to the ground. The average friction offered by the slide is three tenth of his weight. Find (a) the work done by the ladder on the boy as he goes up; (b) the work done by the slide on the boy as he comes down. Neglect any work done by forces inside the body of the boy
A body of mass 0.5 kg travels in a straight line with velocity v = a x3/2 where a = 5 m–1/2s–1. The work done by the net force during its displacement from x = 0 to x = 2 m is ______.
A block of mass 1 kg is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30° by a force of 10 N parallel to the inclined surface (Figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is 0.1. If the block is pushed up by 10 m along the incline, calulate
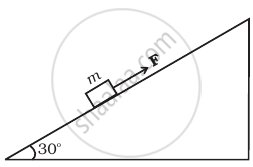
- work done against gravity
- work done against force of friction
- increase in potential energy
- increase in kinetic energy
- work done by applied force.
A cylinder of area 300 cm2 and length 10 cm made of material of specific gravity 0.8 is floated in water with its axis vertical. It is then pushed downward, so as to be just immersed. The work done by the agent who pushes the cylinder into the water is ______ J.
