Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The average separation between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state is 5.3 × 10−11 m. (a) Calculate the Coulomb force between them at this separation. (b) When the atom goes into its first excited state the average separation between the proton and the electron increases to four times its value in the ground state. What is the Coulomb force in this state?
उत्तर
Average separation between the proton and the electron of a Hydrogen atom in ground state, r = 5.3 × 10−11 m
(a) Coulomb force when the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state
\[F = 9 \times {10}^9 \times \frac{q_1 q_2}{r_2}\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times \left( 1 . 6 \times {10}^{- 19} \right)^2}{\left( 5 . 3 \times {10}^{- 11} \right)^2} = 8 . 2 \times {10}^{- 8} \text{N}\]
(b) Coulomb force when the average distance between the proton and the electron becomes 4 times that of its ground state
\[\text {Coulomb force, F } = \frac{1}{4\pi \in_0} = \frac{q_1 q_2}{\left( 4r \right)^2}\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times \left( 1 . 6 \times {10}^{- 19} \right)^2}{16 \times \left( 5 . 3 \right)^2 \times {10}^{- 22}}\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times \left( 1 . 6 \right)^2}{10 \times \left( 5 . 3 \right)^2} \times {10}^{- 7} \]
\[ = 0 . 0512 \times {10}^{- 7} \]
\[ = 5 . 1 \times {10}^{- 9} \text{ N }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A lawyer alleges in court that the police had forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this ?
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
When Neils Bohr shook hand with Werner Heisenberg, what kind of force they exerted ?
Which of the following systems may be adequately described by classical physics ?
(a) motion of a cricket ball
(b) motion of a dust particle
(c) a hydrogen atom
(d) a neutron changing to a proton.
The gravitational force acting on a particle of 1 g due to a similar particle is equal to 6.67 × 10−17 N. Calculate the separation between the particles.
At what distance should two charges, each equal to 1 C, be placed so that the force between them equals your weight ?
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
The magnetic force on a charged particle is always perpendicular to its velocity. Can the magnetic force change the velocity of the particles? Speed of the particle?
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
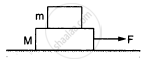
A block of mass m is kept over another block of mass M and the system rests on a horizontal surface (In the following figure). A constant horizontal force F acting on the lower block produces an acceleration \[\frac{F}{2 \left( m + M \right)}\] in the system, and the two blocks always move together. (a) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bigger block and the horizontal surface. (b) Find the frictional force acting on the smaller block. (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the smaller block by the bigger block during a displacement d of the system.
A particle of mass m moves on a straight line with its velocity varying with the distance travelled, according to the equation \[\nu = a\sqrt{x}\] , where a is a constant. Find the total work done by all the forces during a displacement from \[x = 0 \text{ to } x - d\] .
A block of mass 2.0 kg is pushed down an inclined plane of inclination 37° with a force of 20 N acting parallel to the incline. It is found that the block moves on the incline with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If the block started from rest, find the work done (a) by the applied force in the first second, (b) by the weight of the block in the first second and (c) by the frictional force acting on the block in the first second. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

A lawn roller is pulled along a horizontal surface through a distance of 20 m by a rope with a force of 200 N. If the rope makes an angle of 60° with the vertical while pulling, the amount of work done by the pulling force is:
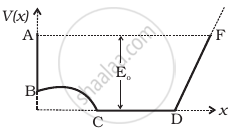
A graph of potential energy V(x) verses x is shown in figure. A particle of energy E0 is executing motion in it. Draw graph of velocity and kinetic energy versus x for one complete cycle AFA.
A block of mass m is taken from A to B slowly under the action of a constant force R Work done by this force is ______.

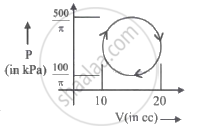
Work done by gas in cyclic process is ______ J.