Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Water falling from a 50-m high fall is to be used for generating electric energy. If \[1 \cdot 8 \times {10}^5 \text{ kg } \] of water falls per hour and half the gravitational potential energy can be converted into electrical energy, how many 100 W lamps can be lit with the generated energy?
उत्तर
Given :
\[\text{ Height, h = 50 m } \]
\[\text{ Mass of water falling per hour, m } = 1 . 8 \times {10}^5 \text{ kg } \]
Power of a lamp,
\[P = 100 \text{ watt } \]
\[\text{ Potential energy of the water }, \]
\[\text{ P . E . = mgh } \]
\[ = 1 . 8 \times {10}^5 \times 9 . 8 \times 50\]
\[ = 882 \times {10}^5 J\]
As only half the potential energy of water is converted into electrical energy,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
A lawyer alleges in court that the police had forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this ?
List all the forces acting on (a) the pulley A, (b) the boy and (c) the block C in figure.
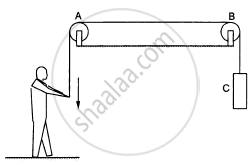
Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
A monkey is sitting on a tree limb. The limb exerts a normal force of 48 N and a frictional force of 20 N. Find the magnitude of the total force exerted by the limb on the monkey.
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A block of mass 5.0 kg slides down an incline of inclination 30° and length 10 m. Find the work done by the force of gravity.
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
A block of mass 250 g slides down an incline of inclination 37° with uniform speed. Find the work done against friction as the block slides through 1m.
A uniform chain of length L and mass M overhangs a horizontal table with its two third part on the table. The friction coefficient between the table and the chain is μ . Find the work done by friction during the period the chain slips off the table.
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y-direction where F is in newton and y in metre. Work done by this force to move the particle from y – 0 to y – 1 m is:
A body is moving unidirectionally under the influence of a source of constant power supplying energy. Which of the diagrams shown in figure correctly shows the displacement-time curve for its motion?
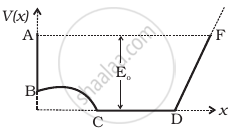
A graph of potential energy V(x) verses x is shown in figure. A particle of energy E0 is executing motion in it. Draw graph of velocity and kinetic energy versus x for one complete cycle AFA.
A block of mass 1 kg is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30° by a force of 10 N parallel to the inclined surface (Figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is 0.1. If the block is pushed up by 10 m along the incline, calulate
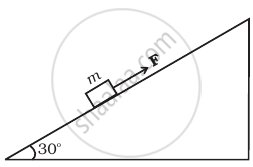
- work done against gravity
- work done against force of friction
- increase in potential energy
- increase in kinetic energy
- work done by applied force.
